Notoginsenoside R1 improves intestinal microvascular functioning in sepsis by targeting Drp1-mediated mitochondrial quality imbalance
- PMID: 38389274
- PMCID: PMC10896147
- DOI: 10.1080/13880209.2024.2318349
Notoginsenoside R1 improves intestinal microvascular functioning in sepsis by targeting Drp1-mediated mitochondrial quality imbalance
Abstract
Context: Sepsis can result in critical organ failure, and notoginsenoside R1 (NGR1) offers mitochondrial protection.
Objective: To determine whether NGR1 improves organ function and prognosis after sepsis by protecting mitochondrial quality.
Materials and methods: A sepsis model was established in C57BL/6 mice using cecum ligation puncture (CLP) and an in vitro model with lipopolysaccharide (LPS, 10 µg/mL)-stimulated primary intestinal microvascular endothelial cells (IMVECs) and then determine NGR1's safe dosage. Groups for each model were: in vivo-a control group, a CLP-induced sepsis group, and a CLP + NGR1 treatment group (30 mg/kg/d for 3 d); in vitro-a control group, a LPS-induced sepsis group, and a LPS + NGR1 treatment group (4 μM for 30 min). NGR1's effects on survival, intestinal function, mitochondrial quality, and mitochondrial dynamic-related protein (Drp1) were evaluated.
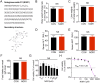
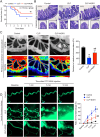
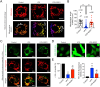
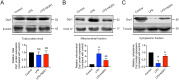
Results: Sepsis resulted in approximately 60% mortality within 7 days post-CLP, with significant reductions in intestinal microvascular perfusion and increases in vascular leakage. Severe mitochondrial quality imbalance was observed in IMVECs. NGR1 (IC50 is 854.1 μM at 30 min) targeted Drp1, inhibiting mitochondrial translocation, preventing mitochondrial fragmentation and restoring IMVEC morphology and function, thus protecting against intestinal barrier dysfunction, vascular permeability, microcirculatory flow, and improving sepsis prognosis.
Discussion and conclusions: Drp1-mediated mitochondrial quality imbalance is a potential therapeutic target for sepsis. Small molecule natural drugs like NGR1 targeting Drp1 may offer new directions for organ protection following sepsis. Future research should focus on clinical trials to evaluate NGR1's efficacy across various patient populations, potentially leading to novel treatments for sepsis.
Keywords: Drp1; Traditional Chinese medicine; mitochondria; sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction mediated through dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1) propagates impairment in blood brain barrier in septic encephalopathy.J Neuroinflammation. 2020 Jan 27;17(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1689-8. J Neuroinflammation. 2020. PMID: 31987040 Free PMC article.
-
Drp1/Fis1 interaction mediates mitochondrial dysfunction in septic cardiomyopathy.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2019 May;130:160-169. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2019.04.006. Epub 2019 Apr 11. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 30981733 Free PMC article.
-
Lipopolysaccharide-induced DNA damage response activates DNA-PKcs to drive actin cytoskeleton disruption and cardiac microvascular dysfunction in endotoxemia.Theranostics. 2025 Apr 28;15(12):5969-5997. doi: 10.7150/thno.111266. eCollection 2025. Theranostics. 2025. PMID: 40365284 Free PMC article.
-
Abnormal mitochondrial fusion-fission balance contributes to the progression of experimental sepsis.Free Radic Res. 2014 Jul;48(7):769-83. doi: 10.3109/10715762.2014.906592. Epub 2014 Apr 10. Free Radic Res. 2014. PMID: 24720571
-
The mitochondrial signature of cultured endothelial cells in sepsis: Identifying potential targets for treatment.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2024 Feb;1870(2):166946. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2023.166946. Epub 2023 Nov 7. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2024. PMID: 37939908 Review.
Cited by
-
Decoding interaction between mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum in ischemic myocardial injury: targeting natural medicines.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Feb 28;16:1536773. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1536773. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40093324 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synergistic effects of notoginsenoside R1 and saikosaponin B2 in atherosclerosis: A novel approach targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and macrophage autophagy.PLoS One. 2025 Jun 27;20(6):e0326687. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0326687. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40577270 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baughman JM, Perocchi F, Girgis HS, Plovanich M, Belcher-Timme CA, Sancak Y, Bao XR, Strittmatter L, Goldberger O, Bogorad RL, et al. . 2011. Integrative genomics identifies MCU as an essential component of the mitochondrial calcium uniporter. Nature. 476(7360):341–345. doi: 10.1038/nature10234. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
