Analysis of the depth of penetration of an epoxy resin-based sealer following a final rinse of irrigants and use of activation systems: An in vitro study
- PMID: 38389742
- PMCID: PMC10880483
- DOI: 10.4103/JCDE.JCDE_221_23
Analysis of the depth of penetration of an epoxy resin-based sealer following a final rinse of irrigants and use of activation systems: An in vitro study
Abstract
Objective: The objective of the study was to compare and evaluate the depth of penetration of an epoxy resin-based sealer following a final rinse of 17% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) and 18% 1-hydroxyethylidene 1, 1-diphosphonate (HEDP), with diode laser and passive ultrasonic activation (PUI): an in vitro confocal laser scanning microscopy study.
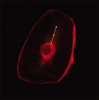
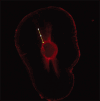
Materials and methods: Fifty-two extracted human mandibular premolar teeth with single root and single canal were selected. They were disinfected in 0.1% thymol solution, cleaned of calculus and soft tissues, and stored in 0.1% thymol solution till use. All teeth were radiographed and selected as per the inclusion and exclusion criteria. The teeth were decoronated using a diamond disk under copious water spray to acquire a standardized root length of 14 mm. Working length was established by inserting a size 10-K file into each root canal until it is visible at the apical foramen and by subtracting 1 mm from the recorded length. Instrumentation of the root canal was done till master apical file size of F3 using ProTaper universal, rotary instruments. The canals were irrigated with 2 mL of 3% sodium hypochlorite between successive files. Teeth were randomly divided into four subgroups n = 12 according to the intervention. Passive ultrasonic irrigation and diode laser were used to activate the irrigants. Final irrigation was performed with distilled water. These specimens were examined using confocal laser scanning microscope (OLYMPUS FLUOVIEW FV 3000) for dentinal tubule penetration of the sealer. Two-way ANOVA test and Tukey's multiple post hoc test were used for statistical analysis.
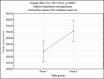
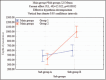
Results: Highly significant difference was seen between the groups with EDTA and HEDP, with HEDP demonstrating the highest penetration. Among the activation techniques used in this study, PUI showed the highest penetration of the sealer. The least penetration was seen with diode laser activation and EDTA.
Conclusions: The irrigation activation techniques significantly influence the penetration of sealer into root dentinal tubules. When penetration of sealer with different irrigation techniques and irrigants was evaluated, significant greater level of sealer penetration was attained with PUI activation of HEDP.
Keywords: 1-diphosphonate; 1-hydroxyethylidene 1; AH plus; confocal laser scanning microscope; dentinal tubule penetration; ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid; rhodamine dye.
Copyright: © 2024 Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Comparative evaluation of effect of N-acetyl cysteine, maleic acid, and ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid on the depth of dentinal tubule penetration of an epoxy resin-based root canal sealer: A confocal laser scanning microscopy study.J Conserv Dent Endod. 2025 Apr;28(4):309-313. doi: 10.4103/JCDE.JCDE_44_25. Epub 2025 Apr 3. J Conserv Dent Endod. 2025. PMID: 40302832 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of different irrigation techniques on the penetration depth of different sealers into dentinal tubules by confocal laser scanning microscope: An in vitro comparative study.J Conserv Dent Endod. 2024 Apr;27(4):388-392. doi: 10.4103/JCDE.JCDE_335_23. Epub 2024 Apr 5. J Conserv Dent Endod. 2024. PMID: 38779208 Free PMC article.
-
To evaluate and compare the effect of 17% EDTA, 10% citric acid, 7% maleic acid on the dentinal tubule penetration depth of bio ceramic root canal sealer using confocal laser scanning microscopy: an in vitro study.F1000Res. 2022 Dec 22;11:1561. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.127091.2. eCollection 2022. F1000Res. 2022. PMID: 36875990 Free PMC article.
-
Dentinal tubule penetration of AH Plus, iRoot SP, MTA fillapex, and guttaflow bioseal root canal sealers after different final irrigation procedures: A confocal microscopic study.Lasers Surg Med. 2016 Jan;48(1):70-6. doi: 10.1002/lsm.22446. Epub 2016 Jan 12. Lasers Surg Med. 2016. PMID: 26774730
-
Influence of Different Types of Root Canal Irrigation Regimen on Resin-based Sealer Penetration and Pushout Bond Strength.Cureus. 2020 Apr 24;12(4):e7807. doi: 10.7759/cureus.7807. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 32467784 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effect of ultrasonic and Er,Cr:YSGG laser-activated irrigation protocol on dual-species root canal biofilm removal: An in vitro study.J Conserv Dent Endod. 2024 Jun;27(6):613-620. doi: 10.4103/JCDE.JCDE_126_24. Epub 2024 Jun 6. J Conserv Dent Endod. 2024. PMID: 38989494 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative evaluation of effect of N-acetyl cysteine, maleic acid, and ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid on the depth of dentinal tubule penetration of an epoxy resin-based root canal sealer: A confocal laser scanning microscopy study.J Conserv Dent Endod. 2025 Apr;28(4):309-313. doi: 10.4103/JCDE.JCDE_44_25. Epub 2025 Apr 3. J Conserv Dent Endod. 2025. PMID: 40302832 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasonic activation of different self-etch adhesive systems - Dentin tubule penetration and push-out bond strength of fiber posts.J Conserv Dent Endod. 2025 Aug;28(8):826-832. doi: 10.4103/JCDE.JCDE_39_25. Epub 2025 Aug 1. J Conserv Dent Endod. 2025. PMID: 40860381 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kuçi A, Alaçam T, Yavaş O, Ergul-Ulger Z, Kayaoglu G. Sealer penetration into dentinal tubules in the presence or absence of smear layer: A confocal laser scanning microscopic study. J Endod. 2014;40:1627–31. - PubMed
-
- Sen BH, Wesselink PR, Türkün M. The smear layer: A phenomenon in root canal therapy. Int Endod J. 1995;28:141–8. - PubMed
-
- Emre Erik C, Onur Orhan E, Maden M. Qualitative analysis of smear layer treated with different etidronate concentrations: A scanning electron microscopy study. Microsc Res Tech. 2019;82:1535–41. - PubMed
-
- Kfir A, Goldenberg C, Metzger Z, Hülsmann M, Baxter S. Cleanliness and erosion of root canal walls after irrigation with a new HEDP-based solution versus traditional sodium hypochlorite followed by EDTA. A scanning electron microscope study. Clin Oral Investig. 2020;24:3699–706. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
