The prospective associations among time management tendency, negative emotions, and problematic smartphone use in Chinese nursing students: enlightenment from COVID-19
- PMID: 38389940
- PMCID: PMC10881827
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1323273
The prospective associations among time management tendency, negative emotions, and problematic smartphone use in Chinese nursing students: enlightenment from COVID-19
Abstract
Purpose: The regularity of epidemic prevention and control measures in China has meant that nursing students have been exposed to more electronic devices, while problematic smartphone use has increased. The purpose of this study is to determine the prospective associations among time management tendency, negative emotions, and problematic smartphone use in nursing students during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods: A longitudinal study was conducted between November 2021 and May 2022. A total of 989 nursing students participated. The convenience sampling method was adopted and the following tools were used: the Adolescence Time Management Disposition Scale, the Depression Anxiety Stress Scales - 21, and the Mobile Phone Addiction Index. Multiple parallel mediation models were used by Mplus.
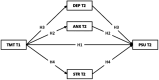
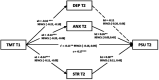
Results: Time management tendency had a significantly negative effect on problematic smartphone use (p < 0.05). Further tests using mediation models showed that stress as a negative emotion mediated the relationship between time management tendency and problematic smartphone use (p < 0.05) over time.
Conclusion: Nursing educators need to strengthen the stress resistance and time management ability of nursing students.
Keywords: COVID-19 pandemic; negative emotions; nursing student; problematic smartphone use; time management tendency.
Copyright © 2024 Ding, Shi, Xu, Wang, Liu, Mao, Zhang and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The relationship between loneliness and problematic smartphone use among adolescents during the COVID-19 pandemic: The mediating role of negative emotions and maladaptive coping.J Adolesc. 2023 Oct;95(7):1449-1462. doi: 10.1002/jad.12218. Epub 2023 Jul 12. J Adolesc. 2023. PMID: 37435881
-
Relationship between depression, anxiety, stress and smartphone addiction in COVID-19 nursing students.Rev Lat Am Enfermagem. 2024 Jan 26;32:e4056. doi: 10.1590/1518-8345.6764.4056. eCollection 2024. Rev Lat Am Enfermagem. 2024. PMID: 38294052 Free PMC article.
-
Anxiety and its relationship with sleep disturbance and problematic smartphone use among Chinese medical students during COVID-19 home confinement - A structural equation model analysis.J Affect Disord. 2022 Jan 1;296:315-321. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2021.09.095. Epub 2021 Oct 1. J Affect Disord. 2022. PMID: 34600968 Free PMC article.
-
Smartphone addiction, risk factors and its adverse effects in nursing students: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Nurse Educ Today. 2021 Mar;98:104741. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2020.104741. Epub 2020 Dec 28. Nurse Educ Today. 2021. PMID: 33485161
-
The negative impact of smartphone usage on nursing students: An integrative literature review.Nurse Educ Today. 2021 Jul;102:104909. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2021.104909. Epub 2021 Apr 17. Nurse Educ Today. 2021. PMID: 33894590 Review.
References
-
- Alsoufi A, Alsuyihili A, Msherghi A, Elhadi A, Atiyah H, Ashini A, et al. . Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on medical education: medical students' knowledge, attitudes, and practices regarding electronic learning. PLoS One. (2020) 15:e0242905. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0242905, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

