Characteristics of Lactobacillus casei probiotic microparticles in L-type methacrylic acid copolymer matrix
- PMID: 38389966
- PMCID: PMC10880912
- DOI: 10.4103/JAPTR.JAPTR_267_23
Characteristics of Lactobacillus casei probiotic microparticles in L-type methacrylic acid copolymer matrix
Abstract
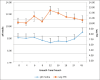
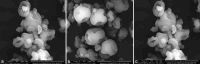
Lactobacillus casei (LC) is a type of lactic acid bacterium that is known for its beneficial probiotic properties. However, it is not typically found in the human intestine because it lacks acid resistance. LC thrives in an optimal pH environment of 6.8 and can be initiated in a more acidic environment at a pH of 3.5. This study purposed to compare the effect of L-type methacrylic acid copolymer (MAC) as a matrix (0.50%, 0.75%, and 1.00%) on the physical characteristics of LC probiotic microparticles made by the spray drying process. Probiotic microparticles were also made from a dry suspension of LC FNCC 0090 bacteria and dispersed in a solution of L-type MAC. The results showed that a rise in matrix content by 1.00% increased particle size (4.47 ± 0.19 µm) and reduced moisture content (7.45 ± 0.11%). The analysis of microparticle morphology also indicated a positive correlation between the level of L-type MAC and the production of smooth, nonporous, and almost spherical shapes. In addition, it was observed that encapsulation efficiency (92.46 ± 0.17%) and protection against stomach acid (98.17% ±1.17%) increased with the level of the matrix.
Keywords: L-type methacrylic acid copolymer; Lactobacillus casei; microencapsulation; probiotic; spray drying.
Copyright: © 2024 Journal of Advanced Pharmaceutical Technology & Research.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Cook MT, Tzortzis G, Charalampopoulos D, Khutoryanskiy VV. Microencapsulation of probiotics for gastrointestinal delivery. J Control Release. 2012;162:56–67. - PubMed
-
- El-Sohaimy SA, Hussain MA. Functional probiotic foods development: Trends, concepts, and products. Fermentation. 2023;9:249.
-
- Arslan S, Erbas M, Tontul I, Topuz A. Microencapsulation of probiotic Saccharomyces cerevisiae var. Boulardii with different wall materials by spray drying. LWT Food Sci Technol. 2015;63:685–90.
-
- Huq T, Khan A, Khan RA, Riedl B, Lacroix M. Encapsulation of probiotic bacteria in biopolymeric system. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2013;53:909–16. - PubMed
-
- Xu M, Gagné-Bourque F, Dumont MJ, Jabaji S. Encapsulation of Lactobacillus casei ATCC 393 cells and evaluation of their survival after freeze-drying, storage and under gastrointestinal conditions. J Food Eng. 2016;168:52–9.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

