Monitoring the metabolite content of seasoned zucchinis during storage by NMR-based metabolomics
- PMID: 38390144
- PMCID: PMC10881322
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25976
Monitoring the metabolite content of seasoned zucchinis during storage by NMR-based metabolomics
Abstract
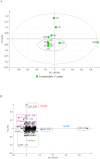
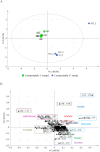
This study applied 1H NMR metabolomics to monitor the metabolite content of baked and seasoned zucchinis packaged in both compostable and plastic trays. Polar extracts of samples stored at 4 °C up to 35 days were investigated to check for metabolite changes upon shelf life. The evolution of the integral values of only the main metabolites responsible for sample differentiation (lactate, acetate, malate, α and β glucose and sucrose) were further analysed and compared. In particular, the evaluation of lactate and acetate amount, considered markers of fermentation progress, showed a comparable performance for the two types of packaging in preserving the freshness of seasoned zucchinis, confirming the maintenance of food product composition within the declared shelf life period in the recommended storage conditions. Albeit preliminary, the results support the NMR metabolomics as a tool for identifying candidate metabolites to monitor the shelf life of foods, thereby improving the understanding of molecular changes during storage.
Keywords: Metabolite; NMR; Packaging; Shelf life; Zucchini.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
-
- De Bruin W., Rossouw W., Korsten L. Comparison of safe alternative dipping treatments to maintain quality of zucchini. J. Food Qual. 2016;39:109–115. doi: 10.1111/jfq.12186. - DOI
-
- Tejada L., Buendía-Moreno L., Villegas A., Cayuela J.M., Bueno-Gavilá E., Gómez P., Abellán A. Nutritional and sensorial characteristics of zucchini (Cucurbita pepo L.) as affected by freezing and the culinary treatment. Int. J. Food Prop. 2020;23:1825–1833. doi: 10.1080/10942912.2020.1826512. - DOI
-
- Iswaldi I., Gómez-Caravaca A.M., Lozano-Sánchez J., Arráez-Román D., Segura-Carretero A., Fernández-Gutiérrez A. Profiling of phenolic and other polar compounds in zucchini (Cucurbita pepo L.) by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Food Res. Int. 2013;50:77–84. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2012.09.030. - DOI
-
- Sgroi F., Piraino F., Donia E. Determinants of ready-to-eat products purchase intentions: an empirical study among the Italian consumers. Hortscience. 2018;53:656–660. doi: 10.21273/HORTSCI12834-17. - DOI
-
- Young N.W.G., O'Sullivan G.R. In: Woodhead Publishing Series in Food Science, Technology and Nutrition, Food and Beverage Stability and Shelf Life. Kilcast David, Subramaniam Persis., editors. Woodhead Publishing; 2011. The influence of ingredients on product stability and shelf life; pp. 132–183. (Chapter 5) - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

