Evaluating palatability in young children: a mini-review of relevant physiology and assessment techniques
- PMID: 38390280
- PMCID: PMC10881860
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2024.1350662
Evaluating palatability in young children: a mini-review of relevant physiology and assessment techniques
Abstract
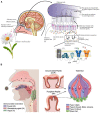
The palatability of pediatric pharmaceutical products plays a crucial role of influencing medication compliance. Rejection of unpalatable medications can potentially lead to treatment failure which can have immediate and delayed consequences. With advances in both the food and pharmaceutical industries, the systematic assessment of palatability has gained importance. Various methods such as visual analogue scales, facial hedonic scales, and facial recognition software, have been employed to assess palatability. While proven to be useful, these methods have significant limitations and may not be workable for young children. Despite these advancements, a universally accepted "gold standard" for assessing pediatric mediation palatability, recognized by drug regulatory agencies, is yet to be established.
Keywords: children; medicine; palatability; taste physiology; viscosity.
© 2024 Schluterman, Linardos, Drulia, Marshall and Kearns.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Shimokawa K, Itabashi T, Yamazaki N, Hino F, Ishii F. Survey of administration methods with view to improving compliance in pediatric patients. J Pharm Health Care Sci. (2009) 35:662–8. 10.5649/jjphcs.35.662 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

