Areas of work-life, psychological capital and emotional intelligence on compassion fatigue and compassion satisfaction among nurses: A cross-sectional study
- PMID: 38391103
- PMCID: PMC10851087
- DOI: 10.1002/nop2.2098
Areas of work-life, psychological capital and emotional intelligence on compassion fatigue and compassion satisfaction among nurses: A cross-sectional study
Abstract
Aim: To examine the impact of six areas of work-life, emotional intelligence and psychological capital on compassion fatigue and compassion satisfaction among Canadian Registered Nurses and licensed practical nurses.
Design: A cross-sectional survey study.
Methods: A convenience sample of 296 Registered Nurses and 110 licensed practical nurses answered a self-administered questionnaire measuring areas of work-life, psychological capital, emotional intelligence, compassion satisfaction and compassion fatigue in September 2019. The association between variables were analysed with descriptive and correlational analyses, while the hypothesized models were tested using multiple regression analyses.
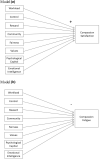
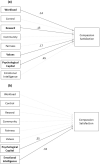
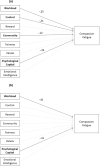
Results: This study identified several areas of work-life and intrapersonal resources that impacted compassion satisfaction and compassion fatigue. Among Registered Nurses, compassion satisfaction was predicted by psychological capital, rewards, values and workload. Compassion fatigue was predicted by psychological capital, workload, control and community. Among licensed practical nurses, compassion satisfaction was predicted by psychological capital and emotional intelligence. Compassion fatigue was predicted by workload and psychological capital. Study results also revealed significant differences in Registered Nurses' and licensed practical nurses' perceptions of workload, rewards and fairness at work, and both compassion satisfaction and compassion fatigue. Registered Nurses perceived their workload to be more manageable and perceived greater rewards and greater fairness at work than licensed practical nurses. Compassion fatigue was higher for Registered Nurses than licensed practical nurses, while compassion satisfaction was higher for licensed practical nurses than Registered Nurses. Future studies should investigate the nature and span of these differences to suggest relevant strategies to mitigate compassion fatigue and promote compassion satisfaction for each of these nursing roles.
Conclusion: The results of this study underscore the need to create nursing work environments that foster a manageable workload and positive social relationships, where nurses have professional autonomy, decision-making capacities and access to adequate resources to do their job effectively. The nursing work environment should also provide recognition of nurses' contributions and an alignment between personal and organizational values. Investments in the development and improvement of nurses' psychological capital and emotional intelligence should be prioritized since they are malleable and impactful intrapersonal resources on compassion satisfaction and compassion fatigue.
Reporting method: This study adhered to the STROBE guidelines.
Public contribution: A total of 406 nurses were involved in this study by answering a self-administered study survey.
Keywords: Registered Nurses; areas of work-life; compassion fatigue; compassion satisfaction; emotional intelligence; licensed practical nurses; psychological capital.
© 2024 The Authors. Nursing Open published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest with respect to the research, authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Relationship Between Psychological Capital and the Occupational Psychologic Risks of Nurses: The Mediation Role of Compassion Satisfaction.J Nurs Scholarsh. 2021 Jan;53(1):115-125. doi: 10.1111/jnu.12607. Epub 2020 Nov 4. J Nurs Scholarsh. 2021. PMID: 33146952
-
Work environmental factors associated with compassion satisfaction and end-of-life care quality among nurses in general wards, palliative care units, and home care settings: A cross-sectional survey.Int J Nurs Stud. 2023 Jul;143:104521. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2023.104521. Epub 2023 Apr 29. Int J Nurs Stud. 2023. PMID: 37201336
-
Factors associated with compassion fatigue and compassion satisfaction in obstetrics and gynaecology nurses: A cross-sectional study.Nurs Open. 2023 Aug;10(8):5509-5520. doi: 10.1002/nop2.1790. Epub 2023 Apr 26. Nurs Open. 2023. PMID: 37099249 Free PMC article.
-
Factors that influence the development of compassion fatigue, burnout, and compassion satisfaction in emergency department nurses.J Nurs Scholarsh. 2015 Mar;47(2):186-94. doi: 10.1111/jnu.12122. Epub 2015 Jan 20. J Nurs Scholarsh. 2015. PMID: 25644276 Review.
-
Extent of compassion satisfaction, compassion fatigue and burnout in nursing: A meta-analysis.J Nurs Manag. 2018 Oct;26(7):810-819. doi: 10.1111/jonm.12589. Epub 2018 Aug 20. J Nurs Manag. 2018. PMID: 30129106 Review.
Cited by
-
Analyzing the correlation between psychological capital in community nurses and their stress management and job satisfaction.BMC Nurs. 2025 May 2;24(1):488. doi: 10.1186/s12912-025-03071-3. BMC Nurs. 2025. PMID: 40316973 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the impact of compassion and leadership on patient safety and quality in healthcare systems: a narrative review.BMJ Open Qual. 2024 May 7;13(Suppl 2):e002651. doi: 10.1136/bmjoq-2023-002651. BMJ Open Qual. 2024. PMID: 38719520 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence and risk factors for intimate partner violence among ICU nurses.BMC Nurs. 2025 Mar 28;24(1):337. doi: 10.1186/s12912-025-03000-4. BMC Nurs. 2025. PMID: 40155896 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al‐Marri, S. S. , Sheppard‐Le Moine, D. , & Stirling, B. (2020). The impact of authentic leadership on nurses' work‐life: A literature review. Archives of Healthcare, 1(1), 37–55. 10.1057/ahc000004 - DOI
-
- Bao, S. , & Taliaferro, D. (2015). Compassion fatigue and psychological capital in nurses working in acute care settings. International Journal for Human Caring, 19(2), 35–40. 10.20467/1091-5710.19.2.35 - DOI
-
- Barzgaran, R. , Farahani, Z. B. , Anboohi, S. Z. , & Eidgahi, E. S. (2019). Investigating the correlation of nurses' compassion fatigue with quality of nursing care from admitted to the emergency department of the selected hospitals of shahid Beheshti university of medical sciences. Journal of International Pharmaceutical Research, 1674(440), 85–94. http://ijprjournals.com/abstractt.php?id=299
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

