Global trends in cutaneous malignant melanoma incidence and mortality
- PMID: 38391175
- PMCID: PMC11045545
- DOI: 10.1097/CMR.0000000000000959
Global trends in cutaneous malignant melanoma incidence and mortality
Abstract
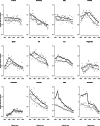
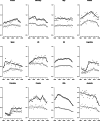
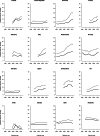
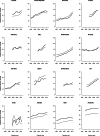
Mortality from cutaneous malignant melanoma (CMM) increased in the past, but trends have been favorable in more recent years in many high-income countries. However, incidence has been increasing in several countries. We provided an up-to-date overview of mortality trends from CMM. We analyzed death certification data from the WHO in selected countries worldwide from 1980 to the most recent available calendar years. We also reported incidence data derived from Cancer Incidence in Five Continents from 1990 to 2012. Separate analyses were performed for young adults aged 20-44 and middle-aged adults aged 45-64 years. Mortality from CMM in all age groups showed a favorable pattern in the majority of the countries considered. Mortality trends declined by 40 to 50% in Australia over the last decades, confirming the importance of prevention measures. Considering young adults aged 20-44, Australia, New Zealand and Northern Europe reported the highest death rates for both sexes (>0.90/100 000 in men and >0.60/100 000 in women) while Japan, the Philippines, and Latin America the lowest ones (<0.50/100 000 and <0.35/100 000 in men and women, respectively). Incidence trends were stable or upward in most countries, with higher rates among women. Our study highlights a global reduction of CMM mortality over the last three decades. The increasing awareness of risk factors, mainly related to UV exposure, along with early diagnosis and progress in treatment for advanced disease played pivotal roles in reducing CMM mortality, particularly in Australia.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Trends in cutaneous malignant melanoma incidence, mortality and survival over three decades: a population-based study in Southern Spain.Clin Exp Dermatol. 2025 Apr 24;50(5):981-993. doi: 10.1093/ced/llae516. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 39576024
-
Recent declines in worldwide mortality from cutaneous melanoma in youth and middle age.Int J Cancer. 1999 Mar 31;81(1):62-6. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0215(19990331)81:1<62::aid-ijc12>3.0.co;2-2. Int J Cancer. 1999. PMID: 10077154
-
Mortality from cutaneous malignant melanoma in Europe. Has the epidemic levelled off?Melanoma Res. 2004 Aug;14(4):301-9. doi: 10.1097/01.cmr.0000136710.75287.1c. Melanoma Res. 2004. PMID: 15305162
-
Cutaneous melanoma.Cancer Surv. 1994;19-20:219-40. Cancer Surv. 1994. PMID: 7534627 Review.
-
Ultraviolet radiation and malignant melanoma.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008;624:104-16. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-77574-6_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008. PMID: 18348451 Review.
Cited by
-
Global, regional, and national burden of cutaneous malignant melanoma from 1990 to 2021 and prediction to 2045.Front Oncol. 2024 Dec 24;14:1512942. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1512942. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39777336 Free PMC article.
-
Pterostilbene as a Multifaceted Anticancer Agent: Molecular Mechanisms, Therapeutic Potential and Future Directions.Med Oncol. 2025 May 24;42(7):220. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02721-5. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40411697 Review.
-
The Prognostic Value of the 31-Gene Expression Profile Test in Cutaneous Melanoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Nov 4;16(21):3714. doi: 10.3390/cancers16213714. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39518150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Melanoma Incidence and Mortality Trends Among Patients Aged 59 Years or Younger in Sweden.JAMA Dermatol. 2024 Nov 1;160(11):1201-1210. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2024.3514. JAMA Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 39245436 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, et al. . Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2021; 71:209–249. - PubMed
-
- Fidler MM, Gupta S, Soerjomataram I, Ferlay J, Steliarova-Foucher E, Bray F. Cancer incidence and mortality among young adults aged 20-39 years worldwide in 2012: a population-based study. Lancet Oncol 2017; 18:1579–1589. - PubMed
-
- Bosetti C, La Vecchia C, Naldi L, Lucchini F, Negri E, Levi F. Mortality from cutaneous malignant melanoma in Europe. Has the epidemic levelled off? Melanoma Res 2004; 14:301–309. - PubMed
-
- Arnold M, de Vries E, Whiteman DC, Jemal A, Bray F, Parkin DM, et al. . Global burden of cutaneous melanoma attributable to ultraviolet radiation in 2012. Int J Cancer 2018; 143:1305–1314. - PubMed

