Contribution of Hfq to gene regulation and virulence in Histophilus somni
- PMID: 38391206
- PMCID: PMC10929436
- DOI: 10.1128/iai.00038-24
Contribution of Hfq to gene regulation and virulence in Histophilus somni
Abstract
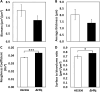
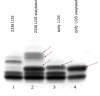
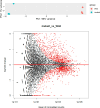
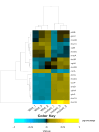
Histophilus somni is one of the predominant bacterial pathogens responsible for bovine respiratory and systemic diseases in cattle. Despite the identification of numerous H. somni virulence factors, little is known about the regulation of such factors. The post-transcriptional regulatory protein Hfq may play a crucial role in regulation of components that affect bacterial virulence. The contribution of Hfq to H. somni phenotype and virulence was investigated following creation of an hfq deletion mutant of H. somni strain 2336 (designated H. somni 2336Δhfq). A comparative analysis of the mutant to the wild-type strain was carried out by examining protein and carbohydrate phenotype, RNA sequence, intracellular survival in bovine monocytes, serum susceptibility, and virulence studies in mouse and calf models. H. somni 2336Δhfq exhibited a truncated lipooligosaccharide (LOS) structure, with loss of sialylation. The mutant demonstrated increased susceptibility to intracellular and serum-mediated killing compared to the wild-type strain. Transcriptomic analysis displayed significant differential expression of 832 upregulated genes and 809 downregulated genes in H. somni 2336Δhfq compared to H. somni strain 2336, including significant downregulation of lsgB and licA, which contribute to LOS oligosaccharide synthesis and sialylation. A substantial number of differentially expressed genes were associated with polysaccharide synthesis and other proteins that could influence virulence. The H. somni 2336Δhfq mutant strain was attenuated in a mouse septicemia model and somewhat attenuated in a calf intrabronchial challenge model. H. somni was recovered less frequently from nasopharyngeal swabs, endotracheal aspirates, and lung tissues of calves challenged with H. somni 2336Δhfq compared to the wild-type strain, and the percentage of abnormal lung tissue in calves challenged with H. somni 2336Δhfq was lower than in calves challenged with the wild-type strain. In conclusion, our results support that Hfq accounts for the regulation of H. somni virulence factors.
Keywords: Hfq; Histophilus somni; biofilm; gene regulation; lipooligosaccharide; virulence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
The role of lipooligosaccharide phosphorylcholine in colonization and pathogenesis of Histophilus somni in cattle.Vet Res. 2012 Jun 7;43(1):49. doi: 10.1186/1297-9716-43-49. Vet Res. 2012. PMID: 22676226 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of luxS in Histophilus somni Virulence and Biofilm Formation.Infect Immun. 2021 Jan 19;89(2):e00567-20. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00567-20. Print 2021 Jan 19. Infect Immun. 2021. PMID: 33139386 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Histophilus somni sialic acid uptake mutant (ΔnanP-ΔnanU) using a mouse septicemia and mortality model.Microb Pathog. 2024 Sep;194:106839. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2024.106839. Epub 2024 Aug 3. Microb Pathog. 2024. PMID: 39103126
-
Histophilus somni: Antigenic and Genomic Changes Relevant to Bovine Respiratory Disease.Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract. 2020 Jul;36(2):279-295. doi: 10.1016/j.cvfa.2020.02.003. Epub 2020 Apr 21. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract. 2020. PMID: 32327251 Review.
-
The Many Facets of Lipooligosaccharide as a Virulence Factor for Histophilus somni.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2016;396:131-48. doi: 10.1007/82_2015_5020. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26814887 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of proteins present in the biofilm matrix and outer membrane vesicles of Histophilus somni during iron-sufficient and iron-restricted growth: identification of potential protective antigens through in silico analyses.mBio. 2025 May 14;16(5):e0064425. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00644-25. Epub 2025 Apr 17. mBio. 2025. PMID: 40243366 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

