Physicochemical Properties of Mixed Gelatin Gels with Soy and Whey Proteins
- PMID: 38391454
- PMCID: PMC10887912
- DOI: 10.3390/gels10020124
Physicochemical Properties of Mixed Gelatin Gels with Soy and Whey Proteins
Abstract
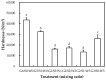
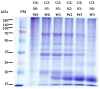
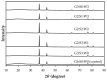
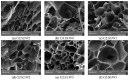
The physicochemical properties of the mixed gelatin gels with soy and whey proteins were investigated to develop the gel base with a soft texture and abundant essential amino acids for the elderly. Gelatin-only gel (control) was prepared at 6% (w/v), and mixed gelatin gels were formulated by replacing gelatin with soy protein isolate and whey protein concentrate at different mixing ratios [gelatin (G):soy protein isolate (S):whey protein concentrate (W)]. Results showed that replacing gelatin with the globular proteins in gelatin gels increased the pH value and processing yield (p < 0.05). Moreover, the mixed gelatin gels, particularly the G2:S1:W3 treatment, showed significantly higher essential amino acids than the gelatin-only control. The partial replacement of gelatin with the globular proteins could decrease the hardness of gelatin gel (p < 0.05), but there was no difference in hardness between the G2:G3:W1, G2:S2:W2, and G2:S1:W3 treatments (p > 0.05). The results of protein pattern, x-ray diffraction, and microstructure had no clear evidence for specific protein-protein interaction in the mixed gelatin gels. Therefore, this study indicates that mixed gelatin gels with the globular proteins at specific mixing ratios could be a practical approach to providing a soft texture and high-level essential amino acids to the elderly.
Keywords: essential amino acid; hardness; jelly food; senior-friendly food.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest in this research article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterizations of emulsion gel formed with the mixture of whey and soy protein and its protein digestion under in vitro gastric conditions.Curr Res Food Sci. 2023 Dec 31;8:100674. doi: 10.1016/j.crfs.2023.100674. eCollection 2024. Curr Res Food Sci. 2023. PMID: 38283161 Free PMC article.
-
[Identification of factors influencing the texture sensitivity of young healthy volunteers based on a model for distinguishing the hardness of an agar-gelatin gel].Vopr Pitan. 2021;90(4):84-93. doi: 10.33029/0042-8833-2021-90-4-84-93. Epub 2021 Jul 22. Vopr Pitan. 2021. PMID: 34538038 Russian.
-
Modification of the structural and rheological properties of whey protein/gelatin mixtures through high pressure processing.Food Chem. 2014 Aug 1;156:243-9. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.01.097. Epub 2014 Feb 5. Food Chem. 2014. PMID: 24629964
-
Color and texture of surimi-like gels made of protein isolate extracted from catfish byproducts are improved by washing and adding soy whey.J Food Sci. 2022 Jul;87(7):3057-3070. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.16229. Epub 2022 Jun 16. J Food Sci. 2022. PMID: 35708220
-
Characterizing acidified and renneted gels with different soy milk and skim milk proportions.Food Res Int. 2023 Oct;172:113207. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2023.113207. Epub 2023 Jun 30. Food Res Int. 2023. PMID: 37689953
Cited by
-
Influence of Gelatin and Propolis Extract on Honey Gummy Jelly Properties: Optimization Using D-Optimal Mixture Design.Gels. 2024 Apr 21;10(4):282. doi: 10.3390/gels10040282. Gels. 2024. PMID: 38667701 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguilera J.M., Park D.J. Texture-modified foods for the elderly: Status, technology and opportunities. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016;57:156–164. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2016.10.001. - DOI
-
- Noh S.W., Song D.H., Yang N.E., Kim H.W. Incorporation of soy protein isolate and egg-white protein to improve nutritional value and hardness of gelatin gels for the elderly. Food Biosci. 2023;53:102806. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2023.102806. - DOI
-
- Gómez-Guillén M.C., Giménez B., López-Caballero M.E., Montero M.P. Functional and bioactive properties of collagen and gelatin from alternative sources: A review. Food Hydrocol. 2011;25:1813–1827. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2011.02.007. - DOI
-
- Alipal J., Mohd Pu’ad N.A.S., Lee T.C., Nayan N.H.M., Sahari N., Basri H., Idis M.I., Abdullah H.Z. A review of gelatin: Properties, sources, process, applications, and commercialization. Mater. Today Proc. 2021;42:240–250. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2020.12.922. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

