Development of End-to-End Artificial Intelligence Models for Surgical Planning in Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion
- PMID: 38391650
- PMCID: PMC10885900
- DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering11020164
Development of End-to-End Artificial Intelligence Models for Surgical Planning in Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion
Abstract
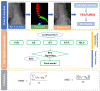
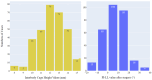
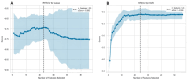
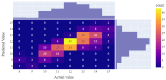
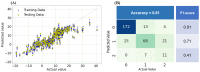
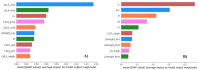
Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) is a commonly used technique for treating lumbar degenerative diseases. In this study, we developed a fully computer-supported pipeline to predict both the cage height and the degree of lumbar lordosis subtraction from the pelvic incidence (PI-LL) after TLIF surgery, utilizing preoperative X-ray images. The automated pipeline comprised two primary stages. First, the pretrained BiLuNet deep learning model was employed to extract essential features from X-ray images. Subsequently, five machine learning algorithms were trained using a five-fold cross-validation technique on a dataset of 311 patients to identify the optimal models to predict interbody cage height and postoperative PI-LL. LASSO regression and support vector regression demonstrated superior performance in predicting interbody cage height and postoperative PI-LL, respectively. For cage height prediction, the root mean square error (RMSE) was calculated as 1.01, and the model achieved the highest accuracy at a height of 12 mm, with exact prediction achieved in 54.43% (43/79) of cases. In most of the remaining cases, the prediction error of the model was within 1 mm. Additionally, the model demonstrated satisfactory performance in predicting PI-LL, with an RMSE of 5.19 and an accuracy of 0.81 for PI-LL stratification. In conclusion, our results indicate that machine learning models can reliably predict interbody cage height and postoperative PI-LL.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; interbody cage; machine learning; sagittal balance; spinal fusion; spinal parameters.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Technical Consideration for TLIF Cage Retrieval and Deformity Correction With Anterior Interbody Fusion in Lumbar Revision Surgeries.Spine Deform. 2019 Jul;7(4):633-640. doi: 10.1016/j.jspd.2018.10.004. Spine Deform. 2019. PMID: 31202382
-
Assessment of radiographic and clinical outcomes of an articulating expandable interbody cage in minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for spondylolisthesis.Neurosurg Focus. 2018 Jan;44(1):E8. doi: 10.3171/2017.10.FOCUS17562. Neurosurg Focus. 2018. PMID: 29290133
-
Does approach matter? A comparative radiographic analysis of spinopelvic parameters in single-level lumbar fusion.Spine J. 2018 Nov;18(11):1999-2008. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2018.03.014. Epub 2018 Apr 6. Spine J. 2018. PMID: 29631061
-
Do intraoperative radiographs predict final lumbar sagittal alignment following single-level transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion?J Neurosurg Spine. 2018 May;28(5):486-491. doi: 10.3171/2017.8.SPINE161231. Epub 2018 Feb 16. J Neurosurg Spine. 2018. PMID: 29451437
-
Restoration of lumbar lordosis after minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a systematic review.Spine J. 2019 May;19(5):951-958. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2018.10.017. Epub 2018 Dec 6. Spine J. 2019. PMID: 30529420
Cited by
-
Prevention and management of degenerative lumbar spine disorders through artificial intelligence-based decision support systems: a systematic review.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025 Feb 7;26(1):126. doi: 10.1186/s12891-025-08356-x. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025. PMID: 39915847 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Intelligence in Surgery: A Systematic Review of Use and Validation.J Clin Med. 2024 Nov 24;13(23):7108. doi: 10.3390/jcm13237108. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39685566 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mummaneni P.V., Dhall S.S., Eck J.C., Groff M.W., Ghogawala Z., Watters W.C., 3rd, Dailey A.T., Resnick D.K., Choudhri T.F., Sharan A., et al. Guideline update for the performance of fusion procedures for degenerative disease of the lumbar spine. Part 11: Interbody techniques for lumbar fusion. J. Neurosurg. Spine. 2014;21:67–74. doi: 10.3171/2014.4.SPINE14276. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Noshchenko A., Hoffecker L., Lindley E.M., Burger E.L., Cain C.M., Patel V.V. Perioperative and long-term clinical outcomes for bone morphogenetic protein versus iliac crest bone graft for lumbar fusion in degenerative disk disease: Systematic review with meta-analysis. J. Spinal Disord. Tech. 2014;27:117–135. doi: 10.1097/01.bsd.0000446752.34233.ca. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

