Digital PCR for Single-Cell Analysis
- PMID: 38391982
- PMCID: PMC10886679
- DOI: 10.3390/bios14020064
Digital PCR for Single-Cell Analysis
Abstract
Single-cell analysis provides an overwhelming strategy for revealing cellular heterogeneity and new perspectives for understanding the biological function and disease mechanism. Moreover, it promotes the basic and clinical research in many fields at a single-cell resolution. A digital polymerase chain reaction (dPCR) is an absolute quantitative analysis technology with high sensitivity and precision for DNA/RNA or protein. With the development of microfluidic technology, digital PCR has been used to achieve absolute quantification of single-cell gene expression and single-cell proteins. For single-cell specific-gene or -protein detection, digital PCR has shown great advantages. So, this review will introduce the significance and process of single-cell analysis, including single-cell isolation, single-cell lysis, and single-cell detection methods, mainly focusing on the microfluidic single-cell digital PCR technology and its biological application at a single-cell level. The challenges and opportunities for the development of single-cell digital PCR are also discussed.
Keywords: digital PCR; microfluidic chip; single-cell analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

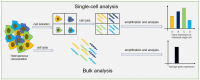

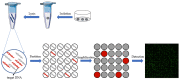
Similar articles
-
A Self-Priming Microfluidic Chip with Cushion Chambers for Easy Digital PCR.Biosensors (Basel). 2021 May 18;11(5):158. doi: 10.3390/bios11050158. Biosensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34069758 Free PMC article.
-
Droplet-Based Digital PCR: Application in Cancer Research.Adv Clin Chem. 2017;79:43-91. doi: 10.1016/bs.acc.2016.10.001. Epub 2016 Dec 27. Adv Clin Chem. 2017. PMID: 28212714
-
Emerging digital PCR technology in precision medicine.Biosens Bioelectron. 2022 Sep 1;211:114344. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2022.114344. Epub 2022 May 14. Biosens Bioelectron. 2022. PMID: 35598553 Review.
-
dPCR: A Technology Review.Sensors (Basel). 2018 Apr 20;18(4):1271. doi: 10.3390/s18041271. Sensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29677144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microfluidic Devices for Forensic DNA Analysis: A Review.Biosensors (Basel). 2016 Aug 5;6(3):41. doi: 10.3390/bios6030041. Biosensors (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27527231 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Microfluidics for the biological analysis of atmospheric ice-nucleating particles: Perspectives and challenges.Biomicrofluidics. 2025 Feb 27;19(1):011502. doi: 10.1063/5.0236911. eCollection 2025 Jan. Biomicrofluidics. 2025. PMID: 40041008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of Digital Polymerase Chain Reaction (dPCR) in Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT).Biomolecules. 2025 Mar 1;15(3):360. doi: 10.3390/biom15030360. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40149896 Free PMC article. Review.
-
S100-positive stroma in salivary gland basal cell adenomas: a neoplastic component with CTNNB1 mutations.Virchows Arch. 2025 May;486(5):1033-1038. doi: 10.1007/s00428-024-04021-1. Epub 2024 Dec 26. Virchows Arch. 2025. PMID: 39724428
-
Generic Reporter Sets for Colorimetric Multiplex dPCR Demonstrated with 6-Plex SNP Quantification Panels.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 17;25(16):8968. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168968. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201654 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative Assessment of Intracellular Effectors and Cellular Response in RAGE Activation.Arch Intern Med Res. 2024;7(2):80-103. doi: 10.26502/aimr.0168. Epub 2024 Apr 26. Arch Intern Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38784044 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dulken B.W., Buckley M.T., Navarro Negredo P., Saligrama N., Cayrol R., Leeman D.S., George B.M., Boutet S.C., Hebestreit K., Pluvinage J.V., et al. Single-cell analysis reveals T cell infiltration in old neurogenic niches. Nature. 2019;571:205–210. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1362-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

