Advances in Respiratory Monitoring: A Comprehensive Review of Wearable and Remote Technologies
- PMID: 38392009
- PMCID: PMC10886711
- DOI: 10.3390/bios14020090
Advances in Respiratory Monitoring: A Comprehensive Review of Wearable and Remote Technologies
Abstract
This article explores the importance of wearable and remote technologies in healthcare. The focus highlights its potential in continuous monitoring, examines the specificity of the issue, and offers a view of proactive healthcare. Our research describes a wide range of device types and scientific methodologies, starting from traditional chest belts to their modern alternatives and cutting-edge bioamplifiers that distinguish breathing from chest impedance variations. We also investigated innovative technologies such as the monitoring of thorax micromovements based on the principles of seismocardiography, ballistocardiography, remote camera recordings, deployment of integrated optical fibers, or extraction of respiration from cardiovascular variables. Our review is extended to include acoustic methods and breath and blood gas analysis, providing a comprehensive overview of different approaches to respiratory monitoring. The topic of monitoring respiration with wearable and remote electronics is currently the center of attention of researchers, which is also reflected by the growing number of publications. In our manuscript, we offer an overview of the most interesting ones.
Keywords: acoustic methods; airflow; impedance; respiration monitoring; thorax movement; wearable devices.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
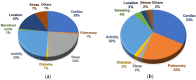

References
-
- Momtazmanesh S., Moghaddam S.S., Ghamari S.-H., Rad E.M., Rezaei N., Shobeiri P., Aali A., Abbasi-Kangevari M., Abbasi-Kangevari Z., Abdelmasseh M., et al. Global Burden of Chronic Respiratory Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990–2019: An Update from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. eClinicalMedicine. 2023;59:101936. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.101936. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation. [(accessed on 27 January 2024)]. Available online: https://vizhub.healthdata.org/
-
- Liu L., Oza S., Hogan D., Chu Y., Perin J., Zhu J., Lawn J.E., Cousens S., Mathers C., Black R.E. Global, Regional, and National Causes of under-5 Mortality in 2000–2015: An Updated Systematic Analysis with Implications for the Sustainable Development Goals. Lancet. 2016;388:3027–3035. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31593-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

