Modulating Golgi Stress Signaling Ameliorates Cell Morphological Phenotypes Induced by CHMP2B with Frontotemporal Dementia-Associated p.Asp148Tyr
- PMID: 38392208
- PMCID: PMC10888485
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb46020090
Modulating Golgi Stress Signaling Ameliorates Cell Morphological Phenotypes Induced by CHMP2B with Frontotemporal Dementia-Associated p.Asp148Tyr
Abstract
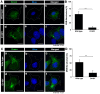
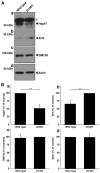
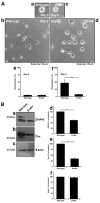
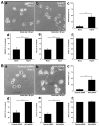
Some charged multivesicular body protein 2B (CHMP2B) mutations are associated with autosomal-dominant neurodegenerative frontotemporal dementia and/or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis type 7 (FTDALS7). The main aim of this study is to clarify the relationship between the expression of mutated CHMP2B protein displaying FTD symptoms and defective neuronal differentiation. First, we illustrate that the expression of CHMP2B with the Asp148Tyr (D148Y) mutation, which preferentially displays FTD phenotypes, blunts neurite process elongation in rat primary cortical neurons. Similar results were observed in the N1E-115 cell line, a model that undergoes neurite elongation. Second, these effects were also accompanied by changes in neuronal differentiation marker protein expression. Third, wild-type CHMP2B protein was indeed localized in the endosomal sorting complexes required to transport (ESCRT)-like structures throughout the cytoplasm. In contrast, CHMP2B with the D148Y mutation exhibited aggregation-like structures and accumulated in the Golgi body. Fourth, among currently known Golgi stress regulators, the expression levels of Hsp47, which has protective effects on the Golgi body, were decreased in cells expressing CHMP2B with the D148Y mutation. Fifth, Arf4, another Golgi stress-signaling molecule, was increased in mutant-expressing cells. Finally, when transfecting Hsp47 or knocking down Arf4 with small interfering (si)RNA, cellular phenotypes in mutant-expressing cells were recovered. These results suggest that CHMP2B with the D148Y mutation, acting through Golgi stress signaling, is negatively involved in the regulation of neuronal cell morphological differentiation, providing evidence that a molecule controlling Golgi stress may be one of the potential FTD therapeutic targets at the molecular and cellular levels.
Keywords: Arf4; CHMP2B; Golgi stress; Hsp47; differentiation.
Conflict of interest statement
Hiroaki Oizumi, Masahiro Yamamoto, and Katsuya Ohbuchi are employed by Tsumura & Co. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
FTD/ALS Type 7-Associated Thr104Asn Mutation of CHMP2B Blunts Neuronal Process Elongation, and Is Recovered by Knockdown of Arf4, the Golgi Stress Regulator.Neurol Int. 2023 Aug 11;15(3):980-993. doi: 10.3390/neurolint15030063. Neurol Int. 2023. PMID: 37606396 Free PMC article.
-
The role of CHMP2BIntron5 in autophagy and frontotemporal dementia.Brain Res. 2016 Oct 15;1649(Pt B):151-157. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2016.02.051. Epub 2016 Mar 10. Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 26972529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Frontotemporal dementia caused by CHMP2B mutation is characterised by neuronal lysosomal storage pathology.Acta Neuropathol. 2015 Oct;130(4):511-23. doi: 10.1007/s00401-015-1475-3. Epub 2015 Sep 10. Acta Neuropathol. 2015. PMID: 26358247 Free PMC article.
-
A transgenic mouse expressing CHMP2Bintron5 mutant in neurons develops histological and behavioural features of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia.Hum Mol Genet. 2016 Aug 1;25(15):3341-3360. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddw182. Epub 2016 Jun 21. Hum Mol Genet. 2016. PMID: 27329763
-
Molecular Genetics of Frontotemporal Dementia Elucidated by Drosophila Models-Defects in Endosomal⁻Lysosomal Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jun 9;19(6):1714. doi: 10.3390/ijms19061714. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29890743 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

