Pedicled Rectus Femoris Flap for Restoration of Suprapatellar Quadriceps Tendon and Defect Coverage after Multiple Reconstruction Attempts-A Case Report and Literature Review
- PMID: 38392570
- PMCID: PMC10889967
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm14020136
Pedicled Rectus Femoris Flap for Restoration of Suprapatellar Quadriceps Tendon and Defect Coverage after Multiple Reconstruction Attempts-A Case Report and Literature Review
Abstract
There is no unified approach for restoring the suprapatellar quadriceps tendon and covering tissue defects simultaneously. In this case report, we present the pedicled myocutaneous rectus femoris flap as one effective approach in two cases with extensive loss or impairment of the suprapatellar muscle-tendon structures after trauma-related suprapatellar quadriceps tendon rupture and multiple reconstruction attempts. Additionally, we provide a literature review of the reconstructive use of the functional pedicled myocutaneous rectus femoris flap.
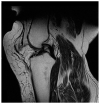
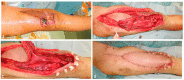
Methods: Two male patients, 48 and 74 years old, with extensive loss or impairment of the suprapatellar muscle-tendon structures due to multiple reconstruction attempts, underwent restoration of the knee extension with a pedicled myocutaneous rectus femoris flap.
Results: Three months after reconstruction, both patients were able to walk freely, unaided. After a six-month follow-up, the free passive mobility of the knee joint was restored, and the active extension of the knee joint was possible in both patients.
Conclusion: The authors conclude that the pedicled rectus femoris flap is a reliable method for the restoration of knee extension, with excellent functional results in cases of suprapatellar tendon lesions. Further to the functional restoration, this technique has the additional advantage of simultaneously achieving coverage of soft-tissue defects, while a direct closure of the donor site is possible. Elderly patients and patients with relevant comorbidities or multiple revisions may especially benefit from this technique.
Keywords: functional reconstruction; pedicled rectus femoris flap; suprapatellar knee extensor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Donor-site morbidity of the pedicled rectus femoris muscle flap.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005 Mar;115(3):786-92. doi: 10.1097/01.prs.0000152422.64505.2a. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005. PMID: 15731680
-
Distally based anteromedial thigh flaps pedicled on the rectus femoris branch of the lateral circumflex femoral artery for reconstruction of soft-tissue defect of the knee.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2018 May;71(5):743-749. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2018.01.007. Epub 2018 Feb 7. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2018. PMID: 29428585
-
Free functional rectus femoris muscle transfer for restoration of knee extension and defect coverage after trauma.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2006;59(9):994-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2005.12.030. Epub 2006 May 2. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2006. PMID: 16920595
-
Combined use of lower medial thigh perforator (LMTP) flap and pedicled medial sural artery perforator flap (MSAP) for lateral knee defects coverage after sarcoma resection: A case report and literature review of soft tissue defect around knee reconstruction.Microsurgery. 2024 Jan;44(1):e31125. doi: 10.1002/micr.31125. Epub 2023 Oct 13. Microsurgery. 2024. PMID: 37830398 Review.
-
[Reconstruction of the extensor apparatus with advanced structural defects in knee revision arthroplasty].Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2022 Apr;34(2):129-140. doi: 10.1007/s00064-021-00746-3. Epub 2021 Nov 4. Oper Orthop Traumatol. 2022. PMID: 34738146 Review. German.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

