Effectiveness and Safety of Biological Therapies in Very Severe Plaque Psoriasis: A Real-Life Retrospective Study
- PMID: 38392619
- PMCID: PMC10890562
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm14020186
Effectiveness and Safety of Biological Therapies in Very Severe Plaque Psoriasis: A Real-Life Retrospective Study
Abstract
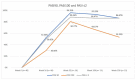
Psoriasis can have a significant impact on quality of life and productivity, especially with increased severity. However, there is limited evidence on biologics' efficacy in highly severe cases compared to moderate-to-severe ones. This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of novel biological therapies in very severe psoriasis. We conducted a retrospective analysis on patients ≥ 18 years old affected by very severe psoriasis who had received a biological agent for at least 16 weeks. We used PASI to assess disease severity and effectiveness at weeks 16, 52, 104, and 156. Safety was evaluated by tracking treatment discontinuation rates and adverse events. This study included 29 males and 11 females, with a mean age of 55.80 years (SD 13.82). Cardiometabolic diseases were the most common comorbidities (25.00%). Twenty-eight (70.00%) patients had psoriasis involvement in at least one difficult-to-treat area. All patients completed 16 weeks of treatment. The mean PASI was 31.60 (SD 2.57) at baseline, 3.48 (SD 4.13) at week 16, 0.58 (SD 1.70) at week 52, 0.77 (SD 1.66) at week 104, and 1.29 (SD 2.12) at week 156. PASI90 and 100 were achieved by 52.50% and 30.00% of patients at week 16, by 96.15% and 80.77% at week 52, by 93.33% and 66.67% at week 104, and by 85.71% and 42.86% at week 156. PASIs ≤ 2 were achieved by 50.00% of patients at week 16, 88.46% at week 52, 86.67% at week 104, and 85.71% at week 156. Only two patients discontinued biologics due to complete remission, and mild AEs were reported by four patients. Our findings show that biologics are effective and well tolerated for treating very severe psoriasis, maintaining long-term effectiveness.
Keywords: PASI; biologics; psoriasis; very severe psoriasis.
Conflict of interest statement
M. Valenti has been a consultant and/or speaker for Sanofi, Leo Pharma, Eli Lilly, Novartis, Janssen, AbbVie, UCB-Pharma, and Boehringer Ingelheim. A. Costanzo has served as an advisory board member and consultant and has received fees and speaker’s honoraria or has participated in clinical trials for Abbvie, Almirall, Biogen, Leo Pharma, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi Genzyme, and UCB-Pharma. A. Narcisi has served on the advisory boards of and received honoraria for lectures and research grants from Almirall, Abbvie, Leo Pharma, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Sanofi-Genzyme, Amgen, and Boehringer Ingelheim. L. Gargiulo has been a consultant for Almirall. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long-term Efficacy and Safety of Up to 108 Weeks of Ixekizumab in Pediatric Patients With Moderate to Severe Plaque Psoriasis: The IXORA-PEDS Randomized Clinical Trial.JAMA Dermatol. 2022 May 1;158(5):533-541. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.0655. JAMA Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 35416908 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Real-Life Effectiveness and Safety of Risankizumab in 131 Patients Affected by Moderate-to-Severe Plaque Psoriasis: A 52-Week Retrospective Study.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2022 Oct;12(10):2309-2324. doi: 10.1007/s13555-022-00795-x. Epub 2022 Sep 5. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2022. PMID: 36063283 Free PMC article.
-
Real-life effectiveness and safety of guselkumab in patients with psoriasis who have an inadequate response to ustekinumab: A 104-week multicenter retrospective study - IL PSO (ITALIAN LANDSCAPE PSORIASIS).J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023 May;37(5):1017-1027. doi: 10.1111/jdv.18913. Epub 2023 Feb 8. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2023. PMID: 36695061
-
Antistreptococcal interventions for guttate and chronic plaque psoriasis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Mar 5;3(3):CD011571. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011571.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 30835819 Free PMC article.
-
Indoor salt water baths followed by artificial ultraviolet B light for chronic plaque psoriasis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 May 5;5(5):CD011941. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011941.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32368795 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prescribing Pattern and Safety Profile of Biological Agents for Psoriasis in Real-World Practice: A Four-Year Calabrian Pharmacovigilance Analysis.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Oct 14;16(10):1329. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16101329. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39458658 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative effectiveness of combined biologic agents versus standard therapies in the treatment of plaque psoriasis: a retrospective analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Sep 18;11:1451069. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1451069. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39359925 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fiorillo G., Ibba L., Gargiulo L., Vignoli C.A., Alfano A., Cortese A., Toso F., Orsini D., Iacovelli P., Frascione P., et al. Effectiveness and safety of anti-IL-23 and anti-IL-17 biological therapies for psoriasis in elderly patients: Real-world experience from two Italian hospitals. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2023;37:e1444–e1446. doi: 10.1111/jdv.19355. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mastorino L., Dapavo P., Susca S., Cariti C., Siliquini N., Verrone A., Stroppiana E., Ortoncelli M., Quaglino P., Ribero S. Drug survival and clinical effectiveness of secukinumab, ixekizumab, brodalumab, guselkumab, risankizumab, tildrakizumab for psoriasis treatment. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2023;22:34–42. doi: 10.1111/ddg.15251. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources