Investigating the Role of Non-Coding RNA in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- PMID: 38392965
- PMCID: PMC10891858
- DOI: 10.3390/ncrna10010010
Investigating the Role of Non-Coding RNA in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Abstract
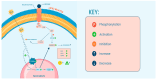
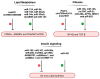
Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) are RNA molecules that do not code for protein but play key roles in regulating cellular processes. NcRNAs globally affect gene expression in diverse physiological and pathological contexts. Functionally important ncRNAs act in chromatin modifications, in mRNA stabilization and translation, and in regulation of various signaling pathways. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a set of conditions caused by the accumulation of triacylglycerol in the liver. Studies of ncRNA in NAFLD are limited but have demonstrated that ncRNAs play a critical role in the pathogenesis of NAFLD. In this review, we summarize NAFLD's pathogenesis and clinical features, discuss current treatment options, and review the involvement of ncRNAs as regulatory molecules in NAFLD and its progression to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). In addition, we highlight signaling pathways dysregulated in NAFLD and review their crosstalk with ncRNAs. Having a thorough understanding of the disease process's molecular mechanisms will facilitate development of highly effective diagnostic and therapeutic treatments. Such insights can also inform preventive strategies to minimize the disease's future development.
Keywords: CircRNA; LncRNA; NAFLD; NASH; PiwiRNA; insulin resistance; metabolic dysfunction; miRNA; ncRNA; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Riazi K., Azhari H., Charette J.H., Underwood F.E., King J.A., Afshar E.E., Swain M.G., Congly S.E., Kaplan G.G., Shaheen A.A. The prevalence and incidence of NAFLD worldwide: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022;7:851–861. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(22)00165-0. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

