The Role of Natural and Synthetic Flavonoids in the Prevention of Marine Biofouling
- PMID: 38393048
- PMCID: PMC10889971
- DOI: 10.3390/md22020077
The Role of Natural and Synthetic Flavonoids in the Prevention of Marine Biofouling
Abstract
Marine biofouling is a major concern for the maritime industry, environment, and human health. Biocides which are currently used in marine coatings to prevent this phenomenon are toxic to the marine environment, and therefore a search for antifoulants with environmentally safe properties is needed. A large number of scientific papers have been published showing natural and synthetic compounds with potential to prevent the attachment of macro- and microfouling marine organisms on submerged surfaces. Flavonoids are a class of compounds which are highly present in nature, including in marine organisms, and have been found in a wide range of biological activities. Some natural and synthetic flavonoids have been evaluated over the last few years for their potential to prevent the settlement and/or the growth of marine organisms on submerged structures, thereby preventing marine biofouling. This review compiles, for the first-time, natural flavonoids as well as their synthetic analogues with attributed antifouling activity against macrofouling and microfouling marine organisms.
Keywords: antifouling activity; biofouling; flavonoids; natural; synthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



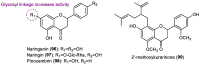
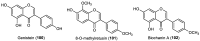

Similar articles
-
Proof of Concept of Natural and Synthetic Antifouling Agents in Coatings.Mar Drugs. 2024 Jun 24;22(7):291. doi: 10.3390/md22070291. Mar Drugs. 2024. PMID: 39057400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Creating New Antifoulants Using the Tools and Tactics of Medicinal Chemistry.Acc Chem Res. 2024 Feb 6;57(3):399-412. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.3c00733. Epub 2024 Jan 26. Acc Chem Res. 2024. PMID: 38277792
-
Current and emerging environmentally-friendly systems for fouling control in the marine environment.Biotechnol Adv. 2013 Dec;31(8):1738-53. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2013.09.002. Epub 2013 Sep 16. Biotechnol Adv. 2013. PMID: 24051087 Review.
-
The marine invasive seaweeds Asparagopsis armata and Sargassum muticum as targets for greener antifouling solutions.Sci Total Environ. 2021 Jan 1;750:141372. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141372. Epub 2020 Aug 7. Sci Total Environ. 2021. PMID: 32853930
-
Natural Benzo/Acetophenones as Leads for New Synthetic Acetophenone Hybrids Containing a 1,2,3-Triazole Ring as Potential Antifouling Agents.Mar Drugs. 2021 Nov 29;19(12):682. doi: 10.3390/md19120682. Mar Drugs. 2021. PMID: 34940681 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Multi-tissue metabolomic profiling reveals the crucial metabolites and pathways associated with scallop growth.BMC Genomics. 2024 Nov 15;25(1):1091. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-11016-4. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39548384 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jin H., Tian L., Bing W., Zhao J., Ren L. Bioinspired marine antifouling coatings: Status, prospects, and future. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2022;124:100889. doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2021.100889. - DOI
-
- Kyei S.K., Darko G., Akaranta O. Chemistry and application of emerging ecofriendly antifouling paints: A review. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2020;17:315–332. doi: 10.1007/s11998-019-00294-3. - DOI
-
- Gomez-Banderas J. Marine Natural Products: A Promising Source of Environmentally Friendly Antifouling Agents for the Maritime Industries. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022;9:858757. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2022.858757. - DOI
-
- Poornima Vijayan P., Formela K., Saeb M.R., Chithra P.G., Thomas S. Integration of antifouling properties into epoxy coatings: A review. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2022;19:269–284. doi: 10.1007/s11998-021-00555-0. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

