FER-like iron deficiency-induced transcription factor (FIT) accumulates in nuclear condensates
- PMID: 38393070
- PMCID: PMC10890924
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.202311048
FER-like iron deficiency-induced transcription factor (FIT) accumulates in nuclear condensates
Abstract
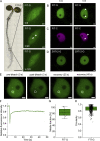
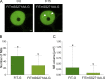
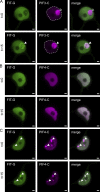
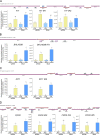
The functional importance of nuclear protein condensation remains often unclear. The bHLH FER-like iron deficiency-induced transcription factor (FIT) controls iron acquisition and growth in plants. Previously described C-terminal serine residues allow FIT to interact and form active transcription factor complexes with subgroup Ib bHLH factors such as bHLH039. FIT has lower nuclear mobility than mutant FITmSS271AA. Here, we show that FIT undergoes a light-inducible subnuclear partitioning into FIT nuclear bodies (NBs). Using quantitative and qualitative microscopy-based approaches, we characterized FIT NBs as condensates that were reversible and likely formed by liquid-liquid phase separation. FIT accumulated preferentially in NBs versus nucleoplasm when engaged in protein complexes with itself and with bHLH039. FITmSS271AA, instead, localized to NBs with different dynamics. FIT colocalized with splicing and light signaling NB markers. The NB-inducing light conditions were linked with active FIT and elevated FIT target gene expression in roots. FIT condensation may affect nuclear mobility and be relevant for integrating environmental and Fe nutrition signals.
© 2024 Trofimov et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: The authors declare no competing interests exist.
Figures











References
-
- Bauer, D., Viczián A., Kircher S., Nobis T., Nitschke R., Kunkel T., Panigrahi K.C.S., Adám E., Fejes E., Schäfer E., and Nagy F.. 2004. Constitutive photomorphogenesis 1 and multiple photoreceptors control degradation of phytochrome interacting factor 3, a transcription factor required for light signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 16:1433–1445. 10.1105/tpc.021568 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

