Botulinum Toxin Injections to the Obliquus Capitis Inferioris Muscle for Dynamic Cervical Dystonia Improves Subjective Patient Outcomes
- PMID: 38393155
- PMCID: PMC10892484
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins16020076
Botulinum Toxin Injections to the Obliquus Capitis Inferioris Muscle for Dynamic Cervical Dystonia Improves Subjective Patient Outcomes
Abstract
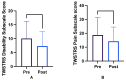
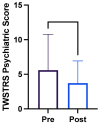
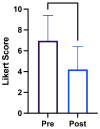
The obliquus capitis inferioris (OCI) muscle is a significant driver of cervical dystonia with torticaput movements and a no-no head tremor. Limited data are available on the efficacy of OCI injections on patient outcomes. Our study aims to determine whether the botulinum toxin injection into OCI improves subjective patient quality of life in those with dystonic head tremors. A retrospective chart review was performed for 25 patients receiving injections into the OCI for a dystonic head tremor at the London Movement Disorders Clinic between January 2020 and January 2022. Toronto Western Spasmodic Torticollis Scale-2 (TWSTRS-2) subscale scores for disability and pain, TWSTRS-PSYCH scores, and the global impression of severity were extracted. The average TWSTRS-2 disability subscale change was -2.8 points (p < 0.003). The average TWSTRS-2 pain subscale change was -4.6 points (p < 0.003). The average TWSTRS-PSYCH score prior to injection was 5.6. After injection, the average score was 3.7 (p < 0.004). The patient self-reported average global impression of severity before injection was 7.0; after this, it was 4.2 (p < 0.0003). The OCI injection showed significant improvement in retrospective patient self-reported outcomes; it should be considered early in the treatment plan for cervical dystonia with a no-no head tremor.
Keywords: botulinum toxin; dystonia; torticollis; tremor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Personalized botulinum toxin type A therapy for cervical dystonia based on kinematic guidance.J Neurol. 2018 Jun;265(6):1269-1278. doi: 10.1007/s00415-018-8819-6. Epub 2018 Mar 20. J Neurol. 2018. PMID: 29557988 Clinical Trial.
-
Torticaput versus Torticollis: Clinical Effects with Modified Classification and Muscle Selection.Tremor Other Hyperkinet Mov (N Y). 2019 Jul 12;9. doi: 10.7916/tohm.v0.647. eCollection 2019. Tremor Other Hyperkinet Mov (N Y). 2019. PMID: 31413892 Free PMC article.
-
Botulinum toxin B: a review of its therapeutic potential in the management of cervical dystonia.Drugs. 2002;62(4):705-22. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200262040-00011. Drugs. 2002. PMID: 11893235 Review.
-
A simplified ultrasonography-guided approach for neurotoxin injection into the obliquus capitis inferior muscle in spasmodic torticollis.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2018 Jul;125(7):1037-1042. doi: 10.1007/s00702-018-1866-4. Epub 2018 Feb 27. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2018. PMID: 29488101 Clinical Trial.
-
Botulinum toxin type A versus anticholinergics for cervical dystonia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 14;4(4):CD004312. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004312.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33852744 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Interdisciplinary Consensus in Evaluating the Severity Subscale of the Original and Revised Toronto Western Spasmodic Torticollis Rating Scale Through Video-Based Assessment: An Inter-Rater Reliability Study.Mov Disord Clin Pract. 2024 Dec;11(12):1587-1591. doi: 10.1002/mdc3.14222. Epub 2024 Oct 8. Mov Disord Clin Pract. 2024. PMID: 39377559
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

