Radiosynthesis, structural identification and in vitro tissue binding study of [18F]FNA-S-ACooP, a novel radiopeptide for targeted PET imaging of fatty acid binding protein 3
- PMID: 38393497
- PMCID: PMC10891031
- DOI: 10.1186/s41181-024-00245-3
Radiosynthesis, structural identification and in vitro tissue binding study of [18F]FNA-S-ACooP, a novel radiopeptide for targeted PET imaging of fatty acid binding protein 3
Abstract
Background: Fatty acid binding protein 3 (FABP3) is a target with clinical relevance and the peptide ligand ACooP has been identified for FABP3 targeting. ACooP is a linear decapeptide containing a free amino and thiol group, which provides opportunities for conjugation. This work is to develop methods for radiolabeling of ACooP with fluorine-18 (18F) for positron emission tomography (PET) applications, and evaluate the binding of the radiolabeled ACooP in human tumor tissue sections with high FABP3 expression.
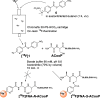
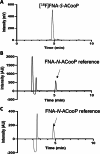
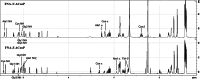
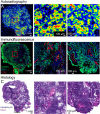
Results: The prosthetic compound 6-[18F]fluoronicotinic acid 4-nitrophenyl ester was conveniently prepared with an on-resin 18F-fluorination in 29.9% radiochemical yield and 96.6% radiochemical purity. Interestingly, 6-[18F]fluoronicotinic acid 4-nitrophenyl ester conjugated to ACooP exclusively by S-acylation instead of the expected N-acylation, and the chemical identity of the product [18F]FNA-S-ACooP was confirmed. In the in vitro binding experiments, [18F]FNA-S-ACooP exhibited heterogeneous and high focal binding in malignant tissue sections, where we also observed abundant FABP3 positivity by immunofluorescence staining. Blocking study further confirmed the [18F]FNA-S-ACooP binding specificity.
Conclusions: FABP3 targeted ACooP peptide was successfully radiolabeled by S-acylation using 6-[18F]fluoronicotinic acid 4-nitrophenyl ester as the prosthetic compound. The tissue binding and blocking studies together with anti-FABP3 immunostaining confirmed [18F]FNA-S-ACooP binding specificity. Further preclinical studies of [18F]FNA-S-ACooP are warranted.
Keywords: ACooP; Autoradiography; Fatty acid binding protein 3; Fluorine-18; PET; Peptide; Peptide radiolabeling; S-acylation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
XGL is an Editorial Board member of EJNMMI Radiopharmacy and Chemistry. Other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
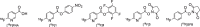
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
