An optimized protocol for the extraction and quantification of cytosolic DNA in mammalian cells
- PMID: 38393950
- PMCID: PMC10901131
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xpro.2024.102913
An optimized protocol for the extraction and quantification of cytosolic DNA in mammalian cells
Abstract
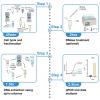
Leakage of mitochondrial or nuclear DNA into the cytosol can occur following viral infections, radiation damage, and some cancers. Here, we present an optimized protocol for isolating and quantifying cytosolic DNA from mammalian cells. We describe steps for collecting cytosolic fractions from cells, extracting DNA using columns, and quantifying extracted DNA using qPCR. This straightforward protocol can be completed in as little as 5 hours, and allows for the identification of the source of DNA. For complete details on the use and execution of this protocol, please refer to Jahun et al.1.
Keywords: Cancer; Cell Biology; Cell separation/fractionation; Cell-based Assays; Immunology; Molecular Biology.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests I.G.G. currently works for Exscientia. However, Exscientia had no involvement in the research presented in this paper or the decision to publish the manuscript.
Figures

References
-
- Aguirre S., Luthra P., Sanchez-Aparicio M.T., Maestre A.M., Patel J., Lamothe F., Fredericks A.C., Tripathi S., Zhu T., Pintado-Silva J., et al. Dengue virus NS2B protein targets cGAS for degradation and prevents mitochondrial DNA sensing during infection. Nat. Microbiol. 2017;2 doi: 10.1038/nmicrobiol.2017.37. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

