Formulation and characterization of glipizide solid dosage form with enhanced solubility
- PMID: 38394326
- PMCID: PMC10890718
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0297467
Formulation and characterization of glipizide solid dosage form with enhanced solubility
Abstract
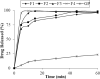
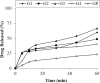
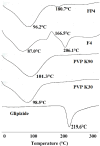
Glipizide, a poor water-soluble drug belongs to BCS class II. The proposed work aimed to enhance the solubility of glipizide by preparing solid dispersions, using polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP) and polyethylene glycol (PEG). Solvent evaporation method was used for the preparation of glipizide solid dispersions. Solid dispersions were prepared in four different drug-to-polymer ratios i.e. 1:1, 1:2, 1:3 and 1:4. Mainly effect of three polymers (PVP K30, PVP K90 and PEG 6000) was evaluated on the solubility and dissolution of glipizide. The in-vitro dissolution of all prepared formulations was performed under pH 6.8 at 37°C using USP type II apparatus. In-vitro dissolution results revealed that the formulations having high concentrations of the polymer showed enhanced solubility. Enhancements in the solubility and rate of dissolution of the drug were noted in solid dispersion formulations compared to the physical blends and pure drug. Solid dispersions containing polyvinyl pyrrolidone exhibited a more favorable pattern of drug release compared to the corresponding solid dispersions with PEG. An increase in the maximum solubility of the drug within the solid dispersion systems was observed in all instances. Two solid dispersion formulations were optimized and formulated into immediate-release tablets, which passed all the pharmacopoeial and non-pharmacopoeial tests. Fourier transformed Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) were used to indicate drug: polymer interactions in solid state. Analysis of the solid dispersion samples through characterization tests indicated the compatibility between the drug and the polymer.
Copyright: © 2024 Alotaibi et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





References
-
- Hörter D, Dressman JB. Influence of physicochemical properties on dissolution of drugs in the gastrointestinal tract. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 1997. Mar 1;25(1):3–14. - PubMed
-
- Wang X, Liu XR, Li KX, Fan X, Liu Y. Effects of ferulic acid on regulating the neurovascular unit: Implications for ischemic stroke treatment. World J Tradit Chin Med 2022;8:210–7.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

