PLA2R-positive membranous nephropathy in IgG4-related disease
- PMID: 38395839
- PMCID: PMC10893645
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-024-03511-3
PLA2R-positive membranous nephropathy in IgG4-related disease
Abstract
Background: IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a fibroinflammatory disease that affects multiple organs, including the pancreas, lacrimal glands, salivary glands, periaortic/retroperitoneum, and kidney. Interstitial nephritis is a typical renal disorder associated with IgG4-RD, but membranous nephropathy is also seen in some cases.
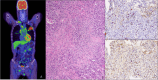
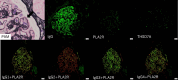
Case presentation: Herein we report on the case of a 77-year-old male patient with nephrotic syndrome and IgG4-related lung disease. His serum phospholipase A2 receptor (PLA2R) antibody was positive. His renal biopsy specimen was also positive for PLA2R. The renal biopsy specimen showed membranous nephropathy with equal IgG3 and IgG4 immunofluorescence staining and no interstitial nephritis, suggesting IgG4-RD manifesting as membranous nephropathy.
Conclusions: Nephrotic syndrome caused by membranous nephropathy is sometimes associated with IgG4-RD. In such cases, even if serum PLA2R antibody is positive, it should be considered that the membranous nephropathy may be secondary to IgG4-RD.
Keywords: IgG4-related Disease; PLA2R-positive membranous nephropathy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests. The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A case of PLA2R-positive membranous nephropathy with subsequent development of IgG4-related disease.CEN Case Rep. 2025 Apr;14(2):280-290. doi: 10.1007/s13730-024-00941-8. Epub 2024 Nov 8. CEN Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 39514162 Free PMC article.
-
Low-density lipoprotein apheresis for PLA2R-related membranous glomerulonephritis accompanied by IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis.CEN Case Rep. 2020 Nov;9(4):395-403. doi: 10.1007/s13730-020-00494-6. Epub 2020 Jun 16. CEN Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 32557252 Free PMC article.
-
A Case of IgG4-Related Disease Manifesting as Extensive Abdominal Periarteritis and Membranous Nephropathy, Successfully Controlled with Low-Dose Steroid Therapy without Relapse or Complications.Nephron. 2025;149(4):213-221. doi: 10.1159/000542414. Epub 2024 Nov 4. Nephron. 2025. PMID: 39496248 Free PMC article.
-
Primary Membranous Nephropathy.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017 Jun 7;12(6):983-997. doi: 10.2215/CJN.11761116. Epub 2017 May 26. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28550082 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IgG4-related kidney disease (IgG4-RKD) with membranous nephropathy as its initial manifestation: report of one case and literature review.BMC Nephrol. 2019 Jul 16;20(1):263. doi: 10.1186/s12882-019-1419-6. BMC Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31311519 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A case of PLA2R-positive membranous nephropathy with subsequent development of IgG4-related disease.CEN Case Rep. 2025 Apr;14(2):280-290. doi: 10.1007/s13730-024-00941-8. Epub 2024 Nov 8. CEN Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 39514162 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

