SHARE-Topic: Bayesian interpretable modeling of single-cell multi-omic data
- PMID: 38395871
- PMCID: PMC10885556
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-024-03180-3
SHARE-Topic: Bayesian interpretable modeling of single-cell multi-omic data
Abstract
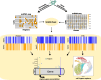
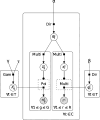
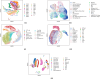
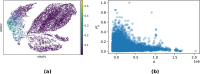
Multi-omic single-cell technologies, which simultaneously measure the transcriptional and epigenomic state of the same cell, enable understanding epigenetic mechanisms of gene regulation. However, noisy and sparse data pose fundamental statistical challenges to extract biological knowledge from complex datasets. SHARE-Topic, a Bayesian generative model of multi-omic single cell data using topic models, aims to address these challenges. SHARE-Topic identifies common patterns of co-variation between different omic layers, providing interpretable explanations for the data complexity. Tested on data from different technological platforms, SHARE-Topic provides low dimensional representations recapitulating known biology and defines associations between genes and distal regulators in individual cells.
Keywords: Bayesian modeling; Gene regulation; Gene regulator in cancer; Interpretability; Lymphoma; Single-cell multi-omics.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Cao J, Cusanovich DA, Ramani V, Aghamirzaie D, Pliner HA, Hill AJ, Daza RM, McFaline-Figueroa JL, Packer JS, Christiansen L, et al. Joint profiling of chromatin accessibility and gene expression in thousands of single cells. Science. 2018;361(6409):1380–1385. doi: 10.1126/science.aau0730. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

