UroPredict: Machine learning model on real-world data for prediction of kidney cancer recurrence (UroCCR-120)
- PMID: 38396089
- PMCID: PMC10891119
- DOI: 10.1038/s41698-024-00532-x
UroPredict: Machine learning model on real-world data for prediction of kidney cancer recurrence (UroCCR-120)
Abstract
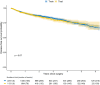
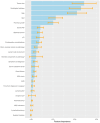
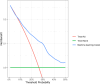
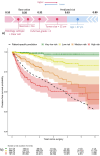
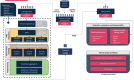
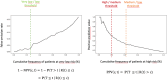
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is most often diagnosed at a localized stage, where surgery is the standard of care. Existing prognostic scores provide moderate predictive performance, leading to challenges in establishing follow-up recommendations after surgery and in selecting patients who could benefit from adjuvant therapy. In this study, we developed a model for individual postoperative disease-free survival (DFS) prediction using machine learning (ML) on real-world prospective data. Using the French kidney cancer research network database, UroCCR, we analyzed a cohort of surgically treated RCC patients. Participating sites were randomly assigned to either the training or testing cohort, and several ML models were trained on the training dataset. The predictive performance of the best ML model was then evaluated on the test dataset and compared with the usual risk scores. In total, 3372 patients were included, with a median follow-up of 30 months. The best results in predicting DFS were achieved using Cox PH models that included 24 variables, resulting in an iAUC of 0.81 [IC95% 0.77-0.85]. The ML model surpassed the predictive performance of the most commonly used risk scores while handling incomplete data in predictors. Lastly, patients were stratified into four prognostic groups with good discrimination (iAUC = 0.79 [IC95% 0.74-0.83]). Our study suggests that applying ML to real-world prospective data from patients undergoing surgery for localized or locally advanced RCC can provide accurate individual DFS prediction, outperforming traditional prognostic scores.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

