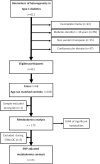
Metabolomic associations of impaired awareness of hypoglycaemia in type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 38396205
- PMCID: PMC10891160
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-55032-6
Metabolomic associations of impaired awareness of hypoglycaemia in type 1 diabetes
Abstract
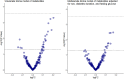
This study investigates impaired awareness of hypoglycaemia (IAH), a complication of insulin therapy affecting 20-40% of individuals with type 1 diabetes. The exact pathophysiology is unclear, therefore we sought to identify metabolic signatures in IAH to elucidate potential pathophysiological pathways. Plasma samples from 578 individuals of the Dutch type 1 diabetes biomarker cohort, 67 with IAH and 108 without IAH (NAH) were analysed using the targeted metabolomics Biocrates AbsoluteIDQ p180 assay. Eleven metabolites were significantly associated with IAH. Genome-wide association studies of these 11 metabolites identified significant single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in C22:1-OH and phosphatidylcholine diacyl C36:6. After adjusting for the SNPs, 11 sphingomyelins and phosphatidylcholines were significantly higher in the IAH group in comparison to NAH. These metabolites are important components of the cell membrane and have been implicated to play a role in cell signalling in diabetes. These findings demonstrate the potential role of phosphatidylcholine and sphingomyelins in IAH.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Geddes J, et al. Prevalence of impaired awareness of hypoglycaemia in adults with Type 1 diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2008;25(4):501–504. - PubMed
-
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee, 6. Glycemic Targets: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2022. Diabetes Care, 2021. 45(Supplement_1): p. S83–S96. - PubMed
-
- Ali N, et al. Fall in prevalence of impaired awareness of hypoglycaemia in individuals with type 1 diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2023;40(4):e15042. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical