Olive Mill Waste-Water Extract Enriched in Hydroxytyrosol and Tyrosol Modulates Host-Pathogen Interaction in IPEC-J2 Cells
- PMID: 38396532
- PMCID: PMC10886184
- DOI: 10.3390/ani14040564
Olive Mill Waste-Water Extract Enriched in Hydroxytyrosol and Tyrosol Modulates Host-Pathogen Interaction in IPEC-J2 Cells
Abstract
The dietary supplementation of olive oil by-products, including olive mill waste-water (OMWW) in animal diets, is a novel application that allows for their re-utilization and recycling and could potentially decrease the use of antibiotics, antimicrobial resistance risk in livestock species, and the occurrence of intestinal diseases. Salmonella serovar typhimurium is one of the most widespread intestinal pathogens in the world, causing enterocolitis in pigs. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of an OMWW extract enriched in polyphenols (hydroxytyrosol and tyrosol) in the immune response of an intestinal porcine epithelial cell line (IPEC-J2) following S. typhimurium infection. Cells were pre-treated with OMWW-extract polyphenols (OMWW-EP, 0.35 and 1.4 µg) for 24 h and then infected with S. typhimurium for 1 h. We evaluated bacterial invasiveness and assayed IPEC-J2 gene expression with RT-qPCR and cytokine release with an ELISA test. The obtained results showed that OMWW-EP (1.4 µg) significantly reduced S. typhimurium invasiveness; 0.35 µg decreased the IPEC-J2 gene expression of IL1B, MYD88, DEFB1 and DEFB4A, while 1.4 µg down-regulated IL1B and DEFB4A and increased TGFB1. The cytokine content was unchanged in infected cells. This is the first study demonstrating the in vitro immunomodulatory and antimicrobial activity of OMWW extracts enriched in polyphenols, suggesting a protective role of OMWW polyphenols on the pig intestine and their potential application as feed supplements in farm animals such as pigs.
Keywords: IPEC-J2; Salmonella spp.; cytokine; defensin; immunomodulation; polyphenols.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

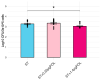



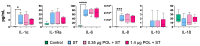
Similar articles
-
Quick assessment of the economic value of olive mill waste water.Chem Cent J. 2016 Oct 17;10:63. doi: 10.1186/s13065-016-0207-7. eCollection 2016. Chem Cent J. 2016. PMID: 27803730 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary supplementation with olive mill wastewaters induces modifications on chicken jejunum epithelial cell transcriptome and modulates jejunum morphology.BMC Genomics. 2018 Aug 2;19(1):576. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4962-9. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 30068314 Free PMC article.
-
Enrichment of Phenolic Compounds from Olive Mill Wastewater and In Vitro Evaluation of Their Antimicrobial Activities.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017;2017:3706915. doi: 10.1155/2017/3706915. Epub 2017 Dec 28. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017. PMID: 29445410 Free PMC article.
-
Salmonella serovar-specific interaction with jejunal epithelial cells.Vet Microbiol. 2017 Aug;207:219-225. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2017.07.002. Epub 2017 Jul 5. Vet Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28757027
-
From antiquity to contemporary times: how olive oil by-products and waste water can contribute to health.Front Nutr. 2023 Oct 16;10:1254947. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1254947. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37908306 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic potential of plant polyphenols in acute pancreatitis.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 Feb;33(2):785-798. doi: 10.1007/s10787-024-01584-y. Epub 2024 Nov 4. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 39497005 Review.
-
Effects of Adding Hydroxytyrosol to the Diet of Pigs in the Nursery Phase on Growth Performance, Biochemical Markers, and Fatty Acid Profile.Animals (Basel). 2025 Aug 1;15(15):2268. doi: 10.3390/ani15152268. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40805058 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Capasso R., Cristinzio G., Evidente A., Scognamiglio F. Isolation, Spectroscopy and Selective Phytotoxic Effects of Polyphenols from Vegetable Waste Waters. Phytochemistry. 1992;31:4125–4128. doi: 10.1016/0031-9422(92)80426-F. - DOI
-
- Ben Sassi A., Boularbah A., Jaouad A., Walker G., Boussaid A. A Comparison of Olive Oil Mill Wastewaters (OMW) from Three Different Processes in Morocco. Process Biochem. 2006;41:74–78. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2005.03.074. - DOI
-
- Casa R., D’Annibale A., Pieruccetti F., Stazi S.R., Giovannozzi Sermanni G., Lo Cascio B. Reduction of the Phenolic Components in Olive-Mill Wastewater by an Enzymatic Treatment and Its Impact on Durum Wheat (Triticum durum Desf.) Germinability. Chemosphere. 2003;50:959–966. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00707-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- El Hadrami A., Belaqziz M., El Hassni M., Hanifi S., Abbad A., Capasso R., Gianfreda L., El Hadrami I. Physico-chemical characterization and effects of olive oil mill wastewaters fertirrigation on the growth of some Mediterranean crops. J. Agron. 2004;3:247–254. doi: 10.3923/ja.2004.247.254. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

