Minimal Residual Disease in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Old and New Concepts
- PMID: 38396825
- PMCID: PMC10889505
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25042150
Minimal Residual Disease in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Old and New Concepts
Abstract
Minimal residual disease (MRD) is of major importance in onco-hematology, particularly in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). MRD measures the amount of leukemia cells remaining in a patient after treatment, and is an essential tool for disease monitoring, relapse prognosis, and guiding treatment decisions. Patients with a negative MRD tend to have superior disease-free and overall survival rates. Considerable effort has been made to standardize MRD practices. A variety of techniques, including flow cytometry and molecular methods, are used to assess MRD, each with distinct strengths and weaknesses. MRD is recognized not only as a predictive biomarker, but also as a prognostic tool and marker of treatment efficacy. Expected advances in MRD assessment encompass molecular techniques such as NGS and digital PCR, as well as optimization strategies such as unsupervised flow cytometry analysis and leukemic stem cell monitoring. At present, there is no perfect method for measuring MRD, and significant advances are expected in the future to fully integrate MRD assessment into the management of AML patients.
Keywords: AML; FlowSOM; LAIP; MRD; NGS; PCR; flow cytometry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
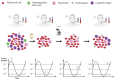
Figures


References
-
- Martens A.C., Van Bekkum D.W., Hagenbeek A. The BN acute myelocytic leukemia (BNML) (a rat model for studying human acute myelocytic leukemia (AML)) Leukemia. 1990;4:241–257. - PubMed
-
- Kumar S., Paiva B., Anderson K.C., Durie B., Landgren O., Moreau P., Munshi N., Lonial S., Bladé J., Mateos M.-V., et al. International Myeloma Working Group consensus criteria for response and minimal residual disease assessment in multiple myeloma. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17:e328–e346. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(16)30206-6. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

