Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Recent Updates
- PMID: 38396884
- PMCID: PMC10889086
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25042208
Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Recent Updates
Abstract
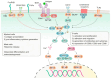
Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitors have revolutionized the landscape for the treatment of hematological malignancies, solid tumors, and, recently, autoimmune disorders. The BTK receptor is expressed in several hematopoietic cells such as macrophages, neutrophils, mast cells, and osteoclasts. Similarly, the BTK receptor is involved in signaling pathways such as chemokine receptor signaling, Toll-like receptor signaling, and Fc receptor signaling. Due to their unique mechanism, these agents provide a diverse utility in a variety of disease states not limited to the field of malignant hematology and are generally well-tolerated.
Keywords: Bruton’s kinase inhibitors; acalabrutinib; autoimmune disorders; hematologic malignancies; ibrutinib; pirtobrutinib; zanubrutinib.
Conflict of interest statement
Jose Sandoval-Sus is a speaker for Seagen, has been a consultant for Massive Bio, and has been on the advisory board for Genmab, AbbVie, Genentech and ADC Therapeutics.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical