A Pharmacological Investigation of the TMEM16A Currents in Murine Skeletal Myogenic Precursor Cells
- PMID: 38396901
- PMCID: PMC10889721
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25042225
A Pharmacological Investigation of the TMEM16A Currents in Murine Skeletal Myogenic Precursor Cells
Abstract
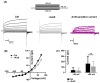
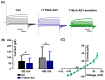
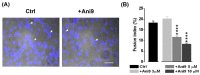
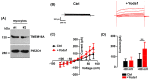
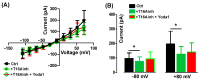
TMEM16A is a Ca2+-activated Cl- channel expressed in various species and tissues. In mammalian skeletal muscle precursors, the activity of these channels is still poorly investigated. Here, we characterized TMEM16A channels and investigated if the pharmacological activation of Piezo1 channels could modulate the TMEM16A currents in mouse myogenic precursors. Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings combined with the pharmacological agents Ani9, T16inh-A01 and Yoda1 were used to characterize TMEM16A-mediated currents and the possible modulatory effect of Piezo1 activity on TMEM16A channels. Western blot analysis was also carried out to confirm the expression of TMEM16A and Piezo1 channel proteins. We found that TMEM16A channels were functionally expressed in fusion-competent mouse myogenic precursors. The pharmacological blockage of TMEM16A inhibited myocyte fusion into myotubes. Moreover, the specific Piezo1 agonist Yoda1 positively regulated TMEM16A currents. The findings demonstrate, for the first time, a sarcolemmal TMEM16A channel activity and its involvement at the early stage of mammalian skeletal muscle differentiation. In addition, the results suggest a possible role of mechanosensitive Piezo1 channels in the modulation of TMEM16A currents.
Keywords: Ani9; Piezo1; TMEM16A; TMEM16inh-A01; Yoda1; myogenesis; skeletal muscle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

