Involvement of Mitochondria in the Selective Response to Microsecond Pulsed Electric Fields on Healthy and Cancer Stem Cells in the Brain
- PMID: 38396911
- PMCID: PMC10889160
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25042233
Involvement of Mitochondria in the Selective Response to Microsecond Pulsed Electric Fields on Healthy and Cancer Stem Cells in the Brain
Abstract
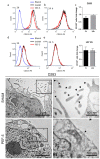
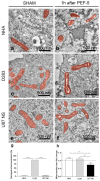
In the last few years, pulsed electric fields have emerged as promising clinical tools for tumor treatments. This study highlights the distinct impact of a specific pulsed electric field protocol, PEF-5 (0.3 MV/m, 40 μs, 5 pulses), on astrocytes (NHA) and medulloblastoma (D283) and glioblastoma (U87 NS) cancer stem-like cells (CSCs). We pursued this goal by performing ultrastructural analyses corroborated by molecular/omics approaches to understand the vulnerability or resistance mechanisms triggered by PEF-5 exposure in the different cell types. Electron microscopic analyses showed that, independently of exposed cells, the main targets of PEF-5 were the cell membrane and the cytoskeleton, causing membrane filopodium-like protrusion disappearance on the cell surface, here observed for the first time, accompanied by rapid cell swelling. PEF-5 induced different modifications in cell mitochondria. A complete mitochondrial dysfunction was demonstrated in D283, while a mild or negligible perturbation was observed in mitochondria of U87 NS cells and NHAs, respectively, not sufficient to impair their cell functions. Altogether, these results suggest the possibility of using PEF-based technology as a novel strategy to target selectively mitochondria of brain CSCs, preserving healthy cells.
Keywords: CD133 protein; cancer stem cells (CSCs); filopodium-like protrusions; glioma; medulloblastoma; mitochondria dysfunction; normal human astrocyte; transcriptomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Microsecond Pulsed Electric Fields: An Effective Way to Selectively Target and Radiosensitize Medulloblastoma Cancer Stem Cells.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021 Apr 1;109(5):1495-1507. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2020.11.047. Epub 2021 Jan 25. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021. PMID: 33509660
-
Effects of Ultra-Short Pulsed Electric Field Exposure on Glioblastoma Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 10;23(6):3001. doi: 10.3390/ijms23063001. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35328420 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Pulsed Electric Fields and Mitochondria-Cytoskeleton Interactions on Cell Respiration.Biophys J. 2018 Jun 19;114(12):2951-2964. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2018.04.047. Biophys J. 2018. PMID: 29925031 Free PMC article.
-
Review of the application of pulsed electric fields (PEF) technology for food processing in China.Food Res Int. 2020 Nov;137:109715. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109715. Epub 2020 Sep 22. Food Res Int. 2020. PMID: 33233287
-
Pulsed electric field-assisted extraction of valuable compounds from microorganisms.Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2020 Mar;19(2):530-552. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12512. Epub 2020 Feb 4. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2020. PMID: 33325176 Review.
References
-
- Novickij V., Rembiałkowska N., Kasperkiewicz-Wasilewska P., Baczyńska D., Rzechonek A., Błasiak P., Kulbacka J. Pulsed electric fields with calcium ions stimulate oxidative alternations and lipid peroxidation in human non-small cell lung cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2022;1864:184055. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2022.184055. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

