Involvement of M1-Activated Macrophages and Perforin/Granulysin Expressing Lymphocytes in IgA Vasculitis Nephritis
- PMID: 38396930
- PMCID: PMC10889255
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25042253
Involvement of M1-Activated Macrophages and Perforin/Granulysin Expressing Lymphocytes in IgA Vasculitis Nephritis
Abstract
We investigated the polarisation of CD68+ macrophages and perforin and granulysin distributions in kidney lymphocyte subsets of children with IgA vasculitis nephritis (IgAVN). Pro-inflammatory macrophage (M)1 (CD68/iNOS) or regulatory M2 (CD68/arginase-1) polarisation; spatial arrangement of macrophages and lymphocytes; and perforin and granulysin distribution in CD3+ and CD56+ cells were visulaised using double-labelled immunofluorescence. In contrast to the tubules, iNOS+ cells were more abundant than the arginase-1+ cells in the glomeruli. CD68+ macrophage numbers fluctuated in the glomeruli and were mostly labelled with iNOS. CD68+/arginase-1+ cells are abundant in the tubules. CD56+ cells, enclosed by CD68+ cells, were more abundant in the glomeruli than in the tubuli, and co-expressed NKp44. The glomerular and interstitial/intratubular CD56+ cells express perforin and granulysin, respectively. The CD3+ cells did not express perforin, while a minority expressed granulysin. Innate immunity, represented by M1 macrophages and CD56+ cells rich in perforin and granulysin, plays a pivotal role in the acute phase of IgAVN.
Keywords: Henoch–Schönlein purpura nephritis; IgA vasculitis nephritis; NK cells; T cells; granulysin; macrophage polarisation; perforin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the study design; collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; writing of the manuscript; or decision to publish the results.
Figures
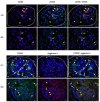
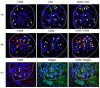
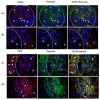
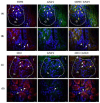
References
-
- Jelusic M., Sestan M., Giani T., Cimaz R. New Insights and Challenges Associated With IgA Vasculitis and IgA Vasculitis With Nephritis—Is It Time to Change the Paradigm of the Most Common Systemic Vasculitis in Childhood? Front. Pediatr. 2022;10:853724. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.853724. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Piram M., Maldini C., Biscardi S., De Suremain N., Orzechowski C., Georget E., Regnard D., Koné-Paut I., Mahr A. Incidence of IgA vasculitis in children estimated by four-source capture-recapture analysis: A population-based study. Rheumatology. 2017;56:1358–1366. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kex158. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jennette J.C., Falk R.J., Bacon P.A., Basu N., Cid M.C., Ferrario F., Flores-Suarez L.F., Gross W.L., Guillevin L., Hagen E.C., et al. Overview of the 2012 revised International Chapel Hill Consensus Conference Nomenclature of Vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65:603–606. doi: 10.1002/art.37715. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

