Genome-Wide Analysis of the Oat (Avena sativa) HSP90 Gene Family Reveals Its Identification, Evolution, and Response to Abiotic Stress
- PMID: 38396983
- PMCID: PMC10889330
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25042305
Genome-Wide Analysis of the Oat (Avena sativa) HSP90 Gene Family Reveals Its Identification, Evolution, and Response to Abiotic Stress
Abstract
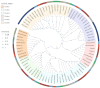
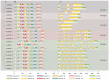
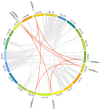
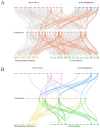
Oats (Avena sativa) are an important cereal crop and cool-season forage worldwide. Heat shock protein 90 (HSP90) is a protein ubiquitously expressed in response to heat stress in almost all plants. To date, the HSP90 gene family has not been comprehensively reported in oats. Herein, we have identified twenty HSP90 genes in oats and elucidated their evolutionary pathways and responses to five abiotic stresses. The gene structure and motif analyses demonstrated consistency across the phylogenetic tree branches, and the groups exhibited relative structural conservation. Additionally, we identified ten pairs of segmentally duplicated genes in oats. Interspecies synteny analysis and orthologous gene identification indicated that oats share a significant number of orthologous genes with their ancestral species; this implies that the expansion of the oat HSP90 gene family may have occurred through oat polyploidization and large fragment duplication. The analysis of cis-acting elements revealed their influential role in the expression pattern of HSP90 genes under abiotic stresses. Analysis of oat gene expression under high-temperature, salt, cadmium (Cd), polyethylene glycol (PEG), and abscisic acid (ABA) stresses demonstrated that most AsHSP90 genes were significantly up-regulated by heat stress, particularly AsHSP90-7, AsHSP90-8, and AsHSP90-9. This study offers new insights into the amplification and evolutionary processes of the AsHSP90 protein, as well as its potential role in response to abiotic stresses. Furthermore, it lays the groundwork for understanding oat adaptation to abiotic stress, contributing to research and applications in plant breeding.
Keywords: HSP90; expression pattern; heat shock protein; oat; phylogenetic analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Exploring Evolutionary Pathways and Abiotic Stress Responses through Genome-Wide Identification and Analysis of the Alternative Oxidase (AOX) Gene Family in Common Oat (Avena sativa).Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 29;25(17):9383. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179383. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273329 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic identification and expression profiling of DMP genes in oat (Avena sativa) elucidate their responsiveness to seed aging.BMC Genomics. 2024 Sep 16;25(1):863. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10743-y. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39285326 Free PMC article.
-
Glutathione S-transferase in mediating adaptive responses of oats (Avena sativa) to osmotic and cadmium stress: genome-wide analysis.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Apr 25;25(1):538. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06559-x. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40281415 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-functionality relationship and modification strategies of oat protein: Challenges and opportunities.Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2025 Jan;24(1):e70091. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.70091. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2025. PMID: 39828399 Review.
-
Research Progress in the Extraction, Structural Characteristics, Bioactivity, and Commercial Applications of Oat β-Glucan: A Review.Foods. 2024 Dec 22;13(24):4160. doi: 10.3390/foods13244160. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39767105 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Profiling of the SPL Transcription Factor Family in Response to Abiotic Stress in Centipedegrass.Plants (Basel). 2024 Dec 28;14(1):62. doi: 10.3390/plants14010062. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39795323 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the HSP90 Gene Family in Relation to Developmental and Abiotic Stress in Ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe).Plants (Basel). 2025 May 29;14(11):1660. doi: 10.3390/plants14111660. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40508332 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification of the Lectin Receptor-like Kinase Gene Family in Avena sativa and Its Role in Salt Stress Tolerance.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 27;25(23):12754. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312754. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684466 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Evolutionary Pathways and Abiotic Stress Responses through Genome-Wide Identification and Analysis of the Alternative Oxidase (AOX) Gene Family in Common Oat (Avena sativa).Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 29;25(17):9383. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179383. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273329 Free PMC article.
-
A global assembly of landrace oat (Avena sativa L.) accessions is a discovery resource for adaptive variation, association mapping, and trait deployment.G3 (Bethesda). 2025 Jun 4;15(6):jkaf093. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkaf093. G3 (Bethesda). 2025. PMID: 40273399 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 32271753/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- SCCXTD-20-1/Sichuan Province Beef Cattle Innovation Team
- 2023YFSY0012/Sichuan Provincial Central and Local University Regional Cooperation Project
- CARS-34/China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA
- sccxtd-2020-16/Sichuan Forage Innovation Team Program
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

