Changes in Cells Associated with Insulin Resistance
- PMID: 38397072
- PMCID: PMC10889819
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25042397
Changes in Cells Associated with Insulin Resistance
Abstract
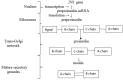
Insulin is a polypeptide hormone synthesized and secreted by pancreatic β-cells. It plays an important role as a metabolic hormone. Insulin influences the metabolism of glucose, regulating plasma glucose levels and stimulating glucose storage in organs such as the liver, muscles and adipose tissue. It is involved in fat metabolism, increasing the storage of triglycerides and decreasing lipolysis. Ketone body metabolism also depends on insulin action, as insulin reduces ketone body concentrations and influences protein metabolism. It increases nitrogen retention, facilitates the transport of amino acids into cells and increases the synthesis of proteins. Insulin also inhibits protein breakdown and is involved in cellular growth and proliferation. On the other hand, defects in the intracellular signaling pathways of insulin may cause several disturbances in human metabolism, resulting in several chronic diseases. Insulin resistance, also known as impaired insulin sensitivity, is due to the decreased reaction of insulin signaling for glucose levels, seen when glucose use in response to an adequate concentration of insulin is impaired. Insulin resistance may cause, for example, increased plasma insulin levels. That state, called hyperinsulinemia, impairs metabolic processes and is observed in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity. Hyperinsulinemia may increase the risk of initiation, progression and metastasis of several cancers and may cause poor cancer outcomes. Insulin resistance is a health problem worldwide; therefore, mechanisms of insulin resistance, causes and types of insulin resistance and strategies against insulin resistance are described in this review. Attention is also paid to factors that are associated with the development of insulin resistance, the main and characteristic symptoms of particular syndromes, plus other aspects of severe insulin resistance. This review mainly focuses on the description and analysis of changes in cells due to insulin resistance.
Keywords: cellular changes associated with insulin resistance; insulin; insulin cellular signaling; insulin resistance; syndromes of insulin resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Insulin Resistance: The Increased Risk of Cancers.Curr Oncol. 2024 Feb 13;31(2):998-1027. doi: 10.3390/curroncol31020075. Curr Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38392069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolism and insulin signaling in common metabolic disorders and inherited insulin resistance.Dan Med J. 2014 Jul;61(7):B4890. Dan Med J. 2014. PMID: 25123125 Review.
-
Cellular Senescence in Diabetes Mellitus: Distinct Senotherapeutic Strategies for Adipose Tissue and Pancreatic β Cells.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Mar 31;13:869414. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.869414. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35432205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disordered fat storage and mobilization in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.Endocr Rev. 2002 Apr;23(2):201-29. doi: 10.1210/edrv.23.2.0461. Endocr Rev. 2002. PMID: 11943743
-
Insulin resistance and Alzheimer's disease: molecular links & clinical implications.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2008 Oct;5(5):438-47. doi: 10.2174/156720508785908919. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2008. PMID: 18855585
Cited by
-
Mechanisms of Insulin Signaling as a Potential Therapeutic Method in Intestinal Diseases.Cells. 2024 Nov 14;13(22):1879. doi: 10.3390/cells13221879. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39594627 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative study of XGBoost and logistic regression for predicting sarcopenia in postsurgical gastric cancer patients.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 14;15(1):12808. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-98075-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40229548 Free PMC article.
-
Daily Brain Metabolic Rhythms of Wild Nocturnal Bats.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 12;25(18):9850. doi: 10.3390/ijms25189850. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337348 Free PMC article.
-
Triglyceride-glucose index: carotid intima-media thickness and cardiovascular risk in a European population.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Jan 13;24(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02574-2. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 39806381 Free PMC article.
-
Early prediction of postpartum dyslipidemia in gestational diabetes using machine learning models.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 7;15(1):8028. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-92299-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40055456 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

