A Genome-Wide Association Study Reveals the Genetic Mechanisms of Nutrient Accumulation in Spinach
- PMID: 38397162
- PMCID: PMC10887921
- DOI: 10.3390/genes15020172
A Genome-Wide Association Study Reveals the Genetic Mechanisms of Nutrient Accumulation in Spinach
Abstract
Spinach is a significant source of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. These nutrients make it delicious and beneficial for human health. However, the genetic mechanism underlying the accumulation of nutrients in spinach remains unclear. In this study, we analyzed the content of chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, oxalate, nitrate, crude fiber, soluble sugars, manganese, copper, and iron in 62 different spinach accessions. Additionally, 3,356,182 high-quality, single-nucleotide polymorphisms were found using resequencing and used in a genome-wide association study. A total of 2077 loci were discovered that significantly correlated with the concentrations of the nutritional elements. Data mining identified key genes in these intervals for four traits: chlorophyll, oxalate, soluble sugar, and Fe. Our study provides insights into the genetic architecture of nutrient variation and facilitates spinach breeding for good nutrition.
Keywords: candidate genes; genome-wide association study; nutrients; single-nucleotide polymorphism; spinach.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
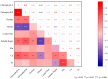
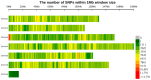
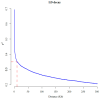

References
-
- van Treuren R., Coquin P., Lohwasser U. Genetic resources collections of leafy vegetables (lettuce, spinach, chicory, artichoke, asparagus, lamb’s lettuce, rhubarb and rocket salad): Composition and gaps. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2012;59:981–997. doi: 10.1007/s10722-011-9738-x. - DOI
-
- Lester G.E., Makus D.J., Hodges D.M., Jifon J.L. Summer (subarctic) versus winter (subtropic) production affects spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) leaf bionutrients: Vitamins (C, E, Folate, K1, provitamin A), lutein, phenolics, and antioxidants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013;61:7019–7027. doi: 10.1021/jf401461z. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Soetan K.O., Olaiya C.O., Oyewole O.E. The importance of mineral elements for humans, domestic animals and plants: A review. Afr. J. Food Sci. 2010;4:200–222. doi: 10.5897/AJFS.9000287. - DOI
-
- Ye S., Shah B.R., Li J., Liang H., Zhan F., Geng F., Li B. A critical review on interplay between dietary fibers and gut microbiota. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022;124:237–249. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2022.04.010. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

