Cross-Species Comparison of the Pan-RAF Inhibitor LY3009120's Anti-Tumor Effects in Equine, Canine, and Human Malignant Melanoma Cell Lines
- PMID: 38397192
- PMCID: PMC10887541
- DOI: 10.3390/genes15020202
Cross-Species Comparison of the Pan-RAF Inhibitor LY3009120's Anti-Tumor Effects in Equine, Canine, and Human Malignant Melanoma Cell Lines
Abstract
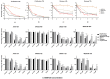
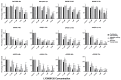
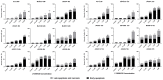
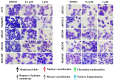
Malignant melanomas (MMs) are the abnormal proliferation of melanocytes and are one of the lethal skin cancers in humans, equines, and canines. Accordingly, MMs in companion animals can serve as naturally occurring animal models, completing conventional cancer models. The common constitutive activation of the MAPK and PI3K pathways in MMs has been described in all three species. Targeting the related pathways is considered a potential option in comparative oncologic approaches. Herein, we present a cross-species comparative analysis exposing a set of ten melanoma cell lines (one human, three equine, and six canine) derived from primary tumors or metastasis to a pan-RAF and RAF dimer inhibitor (LY3009120). Cellular response (proliferation, biomass, metabolism, early and late apoptosis/necrosis, and morphology) and the presence of pathogenic single-nucleotide variants (SNVs) within the mutational hotspot genes BRAF exon 11 and 15, NRAS exon 2 and 3, KRAS exon 2, and KIT exon 11 were analyzed. This study showed that equine malignant melanoma (EMM) cells (MelDuWi) harbor the KRAS p.Q61H mutation, while canine malignant melanoma (CMM) cells (cRGO1 and cRGO1.2) carry NRAS p.G13R. Except for EMM metastasis cells eRGO6 (wild type of the above-mentioned hotspot genes), all melanoma cell lines exhibited a decrease in dose dependence after 48 and 72 h of exposure to LY3009120, independent of the mutation hotspot landscape. Furthermore, LY3009120 caused significant early apoptosis and late apoptosis/necrosis in all melanoma cell lines except for eRGO6. The anti-tumor effects of LY3009120 were observed in nine melanoma cell lines, indicating the potential feasibility of experimental trials with LY3009120. The present study reveals that the irradiation-resistant canine metastasis cells (cRGO1.2) harboring the NRAS p.G13R mutation are significantly LY3009120-sensitive, while the equine metastases-derived eRGO6 cells show significant resistance to LY3009120, which make them both valuable tools for studying resistance mechanisms in comparative oncology.
Keywords: DNA sequencing; LY3009120; Pan-RAF inhibitor; canine malignant melanoma; cellular response; equine malignant melanoma; genetic evaluation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of Pan-RAF Inhibitor LY3009120 on Human Uveal Melanoma Cell Line 92-1.Anticancer Res. 2024 Sep;44(9):3843-3848. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.17210. Anticancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39197916
-
LY3009120, a panRAF inhibitor, has significant anti-tumor activity in BRAF and KRAS mutant preclinical models of colorectal cancer.Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 7;8(6):9251-9266. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14002. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27999210 Free PMC article.
-
RAF inhibitor LY3009120 sensitizes RAS or BRAF mutant cancer to CDK4/6 inhibition by abemaciclib via superior inhibition of phospho-RB and suppression of cyclin D1.Oncogene. 2018 Feb 8;37(6):821-832. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.384. Epub 2017 Oct 23. Oncogene. 2018. PMID: 29059158
-
Targeting oncogenic Raf protein-serine/threonine kinases in human cancers.Pharmacol Res. 2018 Sep;135:239-258. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2018.08.013. Epub 2018 Aug 15. Pharmacol Res. 2018. PMID: 30118796 Review.
-
Targeting NRAS in melanoma.Cancer J. 2012 Mar-Apr;18(2):132-6. doi: 10.1097/PPO.0b013e31824ba4df. Cancer J. 2012. PMID: 22453013 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Canine Models of Human Cancer: Overcoming Drug Resistance Through a Transdisciplinary "One Health, One Medicine" Approach.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jun 17;17(12):2025. doi: 10.3390/cancers17122025. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40563676 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Comparative Oncology of Canine Malignant Melanoma in Targeted Therapy: A Systematic Review of In Vitro Experiments and Animal Model Reports.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 26;25(19):10387. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910387. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408717 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

