Spatiotemporal Expression and Haplotypes Identification of KRT84 Gene and Their Association with Wool Traits in Gansu Alpine Fine-Wool Sheep
- PMID: 38397237
- PMCID: PMC10888427
- DOI: 10.3390/genes15020248
Spatiotemporal Expression and Haplotypes Identification of KRT84 Gene and Their Association with Wool Traits in Gansu Alpine Fine-Wool Sheep
Abstract
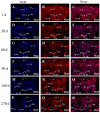
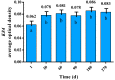
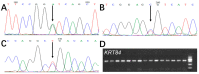
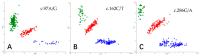
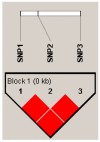
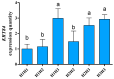
Keratin (K) is a major protein component of hair and is involved in hair growth and development. In this study, we analysed the expression, localization, and polymorphism of the K84 gene (KRT84) in Gansu Alpine Fine-wool sheep using immunofluorescence, RT-qPCR, and PARMS (penta-primer amplification refractory mutation system). Haplotypes of KRT84 were also constructed and their relationship with wool traits analysed. It was revealed that KRT84 was highly expressed in hair follicles, including the inner root sheath, outer root sheath, and hair medulla and at all six lamb ages investigated from 1 to 270 days of age. Three SNPs were detected in KRT84 exon 1, and they formed three haplotypes (named H1, H2, and H3) and six genotypes. Analyses revealed an association between haplotype combinations (diplotypes) and the mean fibre curvature, mean staple length, mean staple strength, mean fibre diameter, the coefficient of variation of fibre diameter, and comfort factor for these sheep. These results suggest that KRT84 is of importance in determining several key traits in Gansu Alpine Fine-wool sheep and that the gene could possibly be used as a genetic marker for wool trait selection in these sheep.
Keywords: Gansu Alpine Fine-wool sheep; SNPs; keratin; spatiotemporal expression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expression Localization of the KRT32 Gene and Its Association of Genetic Variation with Wool Traits.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Mar 30;46(4):2961-2974. doi: 10.3390/cimb46040185. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38666915 Free PMC article.
-
Polymorphism of Keratin Gene KRT71 and Its Relationship with Wool Properties in Gansu Alpine Fine-Wool Sheep.Animals (Basel). 2025 Jul 10;15(14):2028. doi: 10.3390/ani15142028. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40723491 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Genetic Characteristics of the Hoxc13 Gene and Association Analysis of Wool Traits.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 27;25(3):1594. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031594. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338874 Free PMC article.
-
Wool Keratin-Associated Protein Genes in Sheep-A Review.Genes (Basel). 2016 May 28;7(6):24. doi: 10.3390/genes7060024. Genes (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27240405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Major genes and QTL influencing wool production and quality: a review.Genet Sel Evol. 2005;37 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S97-107. doi: 10.1186/1297-9686-37-S1-S97. Genet Sel Evol. 2005. PMID: 15601598 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomic Analysis of Crimped and Straight Wool in Chinese Tan Sheep.Animals (Basel). 2024 Oct 4;14(19):2858. doi: 10.3390/ani14192858. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39409807 Free PMC article.
-
Rumen Development of Tianhua Mutton Sheep Was Better than That of Gansu Alpine Fine Wool Sheep under Grazing Conditions.Animals (Basel). 2024 Apr 23;14(9):1259. doi: 10.3390/ani14091259. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38731263 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Scan for Copy Number Variations in Chinese Merino Sheep Based on Ovine High-Density 600K SNP Arrays.Animals (Basel). 2024 Oct 8;14(19):2897. doi: 10.3390/ani14192897. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39409846 Free PMC article.
-
Ovine KRT81 Variants and Their Influence on Selected Wool Traits of Commercial Value.Genes (Basel). 2024 May 24;15(6):681. doi: 10.3390/genes15060681. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38927617 Free PMC article.
-
Characterisation of Ovine KRTAP19-3 and Its Impact on Wool Traits in Chinese Tan Sheep.Animals (Basel). 2024 Sep 25;14(19):2772. doi: 10.3390/ani14192772. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39409721 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 32060140/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 21JR7RA857/Distinguished Young Scholars Fund of Gansu Province
- GAU-XKTD-2022-21/Discipline Team Project of Gansu Agricultural University
- Gaufx-03Y04/Fuxi Young Talents Fund of Gansu Agricultural University
- 22YF7WA115/Gansu Provincial Key R&D Program Pro-jects
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

