Atomoxetine Treatment of Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Symptoms in 3-6-Year-Old Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Retrospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 38397275
- PMCID: PMC10887200
- DOI: 10.3390/children11020163
Atomoxetine Treatment of Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Symptoms in 3-6-Year-Old Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
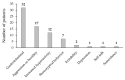
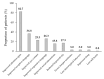
Atomoxetine is indicated for the management of attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children and adolescents aged 6 to 18 years. Few studies have assessed the safety and tolerability of atomoxetine in younger patients. This retrospective cohort study included 133 children aged 3-6 years who were diagnosed with ADHD comorbid with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). The primary endpoint was the evaluation of the safety profile of atomoxetine. In total, 50 patients (37.6%) experienced adverse events (AEs), which led to treatment discontinuation in 23 patients (17.3%). The most common AEs were gastrointestinal (24.1%), aggression or hostility (12.8%), and increased hyperactivity (9.0%). In the 23 patients who discontinued treatment, all the AEs resolved after treatment ceased. Among the 110 patients who completed at least 6 months' treatment, atomoxetine titrated to a dose of 1.2-1.8 mg/kg/day appeared to be well tolerated and effective. The Clinical Global Impression-Improvement score improved to 1 ("very much improved") and 2 ("much improved") in 62.4% and 20.3% of children, respectively, at their last visit. Overall, atomoxetine appeared to be well tolerated in younger children with comorbid ADHD and ASD. Nevertheless, close patient monitoring remains essential, and the study limitations necessitate caution in generalizing these findings to broader populations. Long-term prospective studies are required.
Keywords: adverse events; atomoxetine; attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder; autism spectrum disorder; safety.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A randomized double-blind study of atomoxetine versus placebo for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptoms in children with autism spectrum disorder.J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2012 Jul;51(7):733-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jaac.2012.04.011. Epub 2012 May 25. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 22721596 Clinical Trial.
-
[Atomoxetine: a new treatment for Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in children and adolescents].Encephale. 2005 May-Jun;31(3):337-48. doi: 10.1016/s0013-7006(05)82399-1. Encephale. 2005. PMID: 16142049 Review. French.
-
The Safety of Atomoxetine for the Treatment of Children and Adolescents with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Comprehensive Review of Over a Decade of Research.CNS Drugs. 2016 Jul;30(7):603-28. doi: 10.1007/s40263-016-0349-0. CNS Drugs. 2016. PMID: 27290715 Review.
-
Atomoxetine: a review of its use in attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents.Paediatr Drugs. 2009;11(3):203-26. doi: 10.2165/00148581-200911030-00005. Paediatr Drugs. 2009. PMID: 19445548 Review.
-
Practitioner Review: Pharmacological treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptoms in children and youth with autism spectrum disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2021 Jun;62(6):680-700. doi: 10.1111/jcpp.13305. Epub 2020 Aug 26. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 32845025
Cited by
-
Growing evidence of pharmacotherapy effectiveness in managing attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in young children with or without autism spectrum disorder: a minireview.Front Psychiatry. 2024 Jun 24;15:1408876. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1408876. eCollection 2024. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38979493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Misuse of the Term Retrospective Cohort. Comment on Alsayouf et al. Atomoxetine Treatment of Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Symptoms in 3-6-Year-Old Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Children 2024, 11, 163.Children (Basel). 2024 Dec 19;11(12):1539. doi: 10.3390/children11121539. Children (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39767968 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schachar R.J., Dupuis A., Arnold P.D., Anagnostou E., Kelley E., Georgiades S., Nicolson R., Townes P., Burton C.L., Crosbie J. Autism spectrum disorder and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: Shared or unique neurocognitive profiles? Res. Child Adolesc. Psychopathol. 2023;51:17–31. doi: 10.1007/s10802-022-00958-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wolraich M.L., Hagan J.F., Jr., Allan C., Chan E., Davison D., Earls M., Evans S.W., Flinn S.K., Froehlich T., Frost J., et al. Subcommittee on Children and Adolescents with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactive Disorder. Clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents. Pediatrics. 2019;144:e20192528. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-2528. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5. 5th ed. American Psychiatric Association; Washington, DC, USA: 2013.
-
- Varrasi S., Boccaccio F.M., Guerrera C.S., Platania G.A., Pirrone C., Castellano S. Schooling and occupational outcomes in adults with ADHD: Predictors of success and support strategies for effective learning. Educ. Sci. 2023;13:37. doi: 10.3390/educsci13010037. - DOI
-
- GBD 2019 Mental Disorders Collaborators Global, regional, and national burden of 12 mental disorders in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Psychiatry. 2022;9:137–150. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(21)00395-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

