Paediatric Thoracic Imaging in Cystic Fibrosis in the Era of Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator Modulation
- PMID: 38397368
- PMCID: PMC10888261
- DOI: 10.3390/children11020256
Paediatric Thoracic Imaging in Cystic Fibrosis in the Era of Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator Modulation
Abstract
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is one of the most common progressive life-shortening genetic conditions worldwide. Ground-breaking translational research has generated therapies that target the primary cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) defect, known as CFTR modulators. A crucial aspect of paediatric CF disease is the development and progression of irreversible respiratory disease in the absence of clinical symptoms. Accurate thoracic diagnostics have an important role to play in this regard. Chest radiographs are non-specific and insensitive in the context of subtle changes in early CF disease, with computed tomography (CT) providing increased sensitivity. Recent advancements in imaging hardware and software have allowed thoracic CTs to be acquired in paediatric patients at radiation doses approaching that of a chest radiograph. CFTR modulators slow the progression of CF, reduce the frequency of exacerbations and extend life expectancy. In conjunction with advances in CT imaging techniques, low-dose thorax CT will establish a central position in the routine care of children with CF. International guidelines regarding the choice of modality and timing of thoracic imaging in children with CF are lagging behind these rapid technological advances. The continued progress of personalised medicine in the form of CFTR modulators will promote the emergence of personalised radiological diagnostics.
Keywords: computed tomography; cystic fibrosis; cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator modulator; magnetic resonance imaging; paediatrics; radiography.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
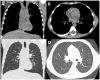
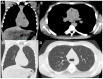
References
-
- Andersen D.H. Cystic Fibrosis of the Pancreas and its Relation to Celiac Disease: A Clinical and Pathologic Study. Am. J. Dis. Child. 1938;56:344–399. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1938.01980140114013. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

