The Complex Interplay between Toxic Hallmark Proteins, Calmodulin-Binding Proteins, Ion Channels, and Receptors Involved in Calcium Dyshomeostasis in Neurodegeneration
- PMID: 38397410
- PMCID: PMC10886625
- DOI: 10.3390/biom14020173
The Complex Interplay between Toxic Hallmark Proteins, Calmodulin-Binding Proteins, Ion Channels, and Receptors Involved in Calcium Dyshomeostasis in Neurodegeneration
Abstract
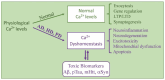
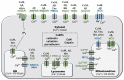
Calcium dyshomeostasis is an early critical event in neurodegeneration as exemplified by Alzheimer's (AD), Huntington's (HD) and Parkinson's (PD) diseases. Neuronal calcium homeostasis is maintained by a diversity of ion channels, buffers, calcium-binding protein effectors, and intracellular storage in the endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, and lysosomes. The function of these components and compartments is impacted by the toxic hallmark proteins of AD (amyloid beta and Tau), HD (huntingtin) and PD (alpha-synuclein) as well as by interactions with downstream calcium-binding proteins, especially calmodulin. Each of the toxic hallmark proteins (amyloid beta, Tau, huntingtin, and alpha-synuclein) binds to calmodulin. Multiple channels and receptors involved in calcium homeostasis and dysregulation also bind to and are regulated by calmodulin. The primary goal of this review is to show the complexity of these interactions and how they can impact research and the search for therapies. A secondary goal is to suggest that therapeutic targets downstream from calcium dyshomeostasis may offer greater opportunities for success.
Keywords: Calmodulin Hypothesis; Tau; alpha-synuclein; amyloid beta; calcium dysregulation; calmodulin-binding proteins; huntingtin; ion channels; neurodegeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Search for a Universal Treatment for Defined and Mixed Pathology Neurodegenerative Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 14;25(24):13424. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413424. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769187 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alzheimer's Disease beyond Calcium Dysregulation: The Complex Interplay between Calmodulin, Calmodulin-Binding Proteins and Amyloid Beta from Disease Onset through Progression.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Jul 27;45(8):6246-6261. doi: 10.3390/cimb45080393. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37623212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein Biomarkers Shared by Multiple Neurodegenerative Diseases Are Calmodulin-Binding Proteins Offering Novel and Potentially Universal Therapeutic Targets.J Clin Med. 2023 Nov 11;12(22):7045. doi: 10.3390/jcm12227045. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 38002659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calmodulin binding proteins and neuroinflammation in multiple neurodegenerative diseases.BMC Neurosci. 2022 Mar 4;23(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s12868-022-00695-y. BMC Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35246032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Broad neutralization of calcium-permeable amyloid pore channels with a chimeric Alzheimer/Parkinson peptide targeting brain gangliosides.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Feb;1862(2):213-22. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2015.11.012. Epub 2015 Dec 2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26655601
Cited by
-
Cannabinoid regulation of angiotensin II-induced calcium signaling in striatal neurons.NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2024 Nov 15;10(1):220. doi: 10.1038/s41531-024-00827-7. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2024. PMID: 39548112 Free PMC article.
-
Modulating intracellular calcium dynamics with alkaloids: A novel strategy against oxidative neurodegeneration.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2025 Jul 27;14(4):tfaf100. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfaf100. eCollection 2025 Aug. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2025. PMID: 40718852 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium and Non-Penetrating Traumatic Brain Injury: A Proposal for the Implementation of an Early Therapeutic Treatment for Initial Head Insults.Biomolecules. 2024 Jul 15;14(7):853. doi: 10.3390/biom14070853. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39062567 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Search for a Universal Treatment for Defined and Mixed Pathology Neurodegenerative Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 14;25(24):13424. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413424. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769187 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The calmodulin hypothesis of neurodegenerative diseases: searching for a common cure.Neurodegener Dis Manag. 2025 Apr-Jun;15(2-3):113-115. doi: 10.1080/17582024.2025.2488230. Epub 2025 Apr 2. Neurodegener Dis Manag. 2025. PMID: 40173153 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

