From Host Defense to Metabolic Signatures: Unveiling the Role of γδ T Cells in Bacterial Infections
- PMID: 38397462
- PMCID: PMC10886488
- DOI: 10.3390/biom14020225
From Host Defense to Metabolic Signatures: Unveiling the Role of γδ T Cells in Bacterial Infections
Abstract
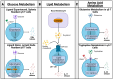
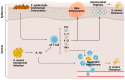
The growth of antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections necessitates focusing on host-derived immunotherapies. γδ T cells are an unconventional T cell subset, making up a relatively small portion of healthy circulating lymphocytes but a substantially increased proportion in mucosal and epithelial tissues. γδ T cells are activated and expanded in response to bacterial infection, having the capability to produce proinflammatory cytokines to recruit neutrophils and clear infection. They also play a significant role in dampening immune response to control inflammation and protecting the host against secondary challenge, making them promising targets when developing immunotherapy. Importantly, γδ T cells have differential metabolic states influencing their cytokine profile and subsequent inflammatory capacity. Though these differential metabolic states have not been well studied or reviewed in the context of bacterial infection, they are critical in understanding the mechanistic underpinnings of the host's innate immune response. Therefore, this review will focus on the context-specific host defense conferred by γδ T cells during infection with Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Listeria monocytogenes, and Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Keywords: bacterial infection; immunometabolism; γδ T cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mice Lacking γδ T Cells Exhibit Impaired Clearance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Lung Infection and Excessive Production of Inflammatory Cytokines.Infect Immun. 2020 May 20;88(6):e00171-20. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00171-20. Print 2020 May 20. Infect Immun. 2020. PMID: 32229615 Free PMC article.
-
IL-17A-producing resident memory γδ T cells orchestrate the innate immune response to secondary oral Listeria monocytogenes infection.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Jul 26;113(30):8502-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1600713113. Epub 2016 Jul 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27402748 Free PMC article.
-
Gammadelta T lymphocytes producing IFNgamma and IL-17 in response to Candida albicans or mycobacterial antigens: possible implications for acute and chronic inflammation.Curr Med Chem. 2009;16(35):4743-9. doi: 10.2174/092986709789878238. Curr Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19903136 Review.
-
Importance of murine Vdelta1gammadelta T cells expressing interferon-gamma and interleukin-17A in innate protection against Listeria monocytogenes infection.Immunology. 2008 Oct;125(2):170-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2008.02841.x. Epub 2008 Apr 7. Immunology. 2008. PMID: 18397272 Free PMC article.
-
Human and murine memory γδ T cells: Evidence for acquired immune memory in bacterial and viral infections and autoimmunity.Cell Immunol. 2020 Nov;357:104217. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2020.104217. Epub 2020 Sep 16. Cell Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32979762 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kabelitz D., Wesch D., Hinz T. Springer Seminars in Immunopathology. Volume 21. Springer International; Berlin, Germany: 1999. Gamma Delta T Cells, Their T Cell Receptor Usage and Role in Human Diseases; pp. 55–75. - PubMed
-
- Brown A.F., Murphy A.G., Lalor S.J., Leech J.M., O’Keeffe K.M., Mac Aogáin M., O’Halloran D.P., Lacey K.A., Tavakol M., Hearnden C.H., et al. Memory Th1 Cells Are Protective in Invasive Staphylococcus aureus Infection. PLoS Pathog. 2015;11:e1005226. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005226. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

