Enhancing Bromelain Recovery from Pineapple By-Products: A Sustainable Approach for Value Addition and Waste Reduction
- PMID: 38397568
- PMCID: PMC10888004
- DOI: 10.3390/foods13040589
Enhancing Bromelain Recovery from Pineapple By-Products: A Sustainable Approach for Value Addition and Waste Reduction
Abstract
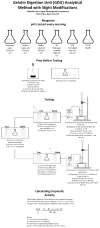
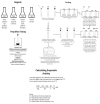
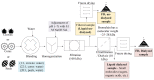
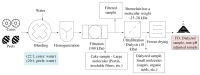
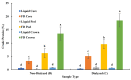
Pineapple by-products are good sources of bromelain, a complex enzyme with commercial applications. This study evaluated the feasibility of producing bromelain powders from pineapple waste using an organic solvent-free approach. Pineapple by-products (from var. MD2), including cores, peels, crowns, stems, and basal stems, were homogenized with deionized water, and the pH of the mixture was adjusted to 4.5 and 9 (isoelectric points of fruit bromelain and stem bromelain), clarified, ultra-filtered, and freeze-dried to produce bromelain powders. The enzymatic activity of the bromelain powders was measured using the gelatin and casein digestion methods. The bromelain powders from the crowns did not show significant enzymatic activity (p < 0.05). Meanwhile, bromelain powders produced from the cores and peels had an enzymatic activity of 694 gelatin digesting units (GDU)/g and 124 casein digesting units (CDU)/mg, and 1179 GDU/g and 217 CDU/mg, respectively. Bromelain powders from the basal stems showed the highest enzymatic activity (2909 GDU/g and 717 CDU/mg). Increasing the pH of the liquid mixture before the purification and freeze drying significantly (p < 0.05) reduced the enzymatic activity of the bromelain powders. Using a practical and organic solvent-free approach, this study demonstrates the feasibility of producing bromelain powders with high enzymatic activity from pineapple waste.
Keywords: bromelain; dialysis; enzymatic activity; pineapple by-products; upcycling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships, which may be considered as potential competing interests: K. Mis Solval reports financial support provided by Del Monte Fresh Produce NA to conduct this study. B. Martinez and T. Nakamura participated in the conceptualization and experimental design but did not play an active role in the investigation, data collection, or analysis.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Integral Valorization of Pineapple (Ananas comosus L.) By-Products through a Green Chemistry Approach towards Added Value Ingredients.Foods. 2020 Jan 7;9(1):60. doi: 10.3390/foods9010060. Foods. 2020. PMID: 31936041 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and Potential Application of Bromelain from Pineapple (Ananas comosus) Waste (Peel) in Recovery of Silver from X-Ray Films.Int J Biomater. 2021 Nov 17;2021:9964337. doi: 10.1155/2021/9964337. eCollection 2021. Int J Biomater. 2021. PMID: 34840577 Free PMC article.
-
Fractionation and activity profiling of fruit bromelain from pineapples of Phuket variety growing in Thailand.J Food Biochem. 2019 Nov;43(11):e13011. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.13011. Epub 2019 Aug 8. J Food Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31393018
-
Microbial biotechnology approaches for conversion of pineapple waste in to emerging source of healthy food for sustainable environment.Int J Food Microbiol. 2022 Jul 16;373:109714. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2022.109714. Epub 2022 May 7. Int J Food Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35567891 Review.
-
Nutritional Composition and Therapeutic Potential of Pineapple Peel - A Comprehensive Review.Chem Biodivers. 2024 May;21(5):e202400315. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202400315. Epub 2024 Apr 11. Chem Biodivers. 2024. PMID: 38484117 Review.
References
-
- Nor M.Z.M., Ramchandran L., Duke M., Vasiljevic T. Characteristic properties of crude pineapple waste extract for bromelain purification by membrane processing. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015;52:7103–7112. doi: 10.1007/s13197-015-1812-5. - DOI
-
- Banerjee S., Ranganathan V., Patti A., Arora A. Valorisation of pineapple wastes for food and therapeutic applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018;82:60–70. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2018.09.024. - DOI
-
- Imandi S.B., Bandaru V.V.R., Somalanka S.R., Bandaru S.R., Garapati H.R. Application of statistical experimental designs for the optimization of medium constituents for the production of citric acid from pineapple waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2008;99:4445–4450. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2007.08.071. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

