The Association between Functional Dyspepsia and Metabolic Syndrome-The State of the Art
- PMID: 38397726
- PMCID: PMC10888556
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph21020237
The Association between Functional Dyspepsia and Metabolic Syndrome-The State of the Art
Abstract
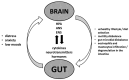
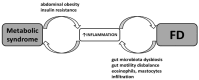
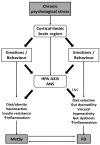
Functional dyspepsia is a common functional disorder of the gastrointestinal tract that is responsible for many primary care visits. No organic changes have been found to explain its symptoms. We hypothesize that modern lifestyles and environmental factors, especially psychological stress, play a crucial role in the high prevalence of functional dyspepsia and metabolic syndrome. While gastrointestinal tract diseases are rarely linked to metabolic disorders, chronic stress, obesity-related metabolic syndrome, chronic inflammation, intestinal dysbiosis, and functional dyspepsia have significant pathophysiological associations. Functional dyspepsia, often associated with anxiety and chronic psychological stress, can activate the neuroendocrine stress axis and immune system, leading to unhealthy habits that contribute to obesity. Additionally, intestinal dysbiosis, which is commonly present in functional dyspepsia, can exacerbate systemic inflammation and obesity, further promoting metabolic syndrome-related disorders. It is worth noting that the reverse is also true: obesity-related metabolic syndrome can worsen functional dyspepsia and its associated symptoms by triggering systemic inflammation and intestinal dysbiosis, as well as negative emotions (depression) through the brain-gut axis. To understand the pathophysiology and deliver an effective treatment strategy for these two difficult-to-cure disorders, which are challenging for both caregivers and patients, a psychosocial paradigm is essential.
Keywords: feeding behavior; gastrointestinal diseases; gastrointestinal microbiome; metabolic syndrome; psychological; stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Is there a causal link between psychological disorders and functional gastrointestinal disorders?Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Nov;14(11):1047-1059. doi: 10.1080/17474124.2020.1801414. Epub 2020 Aug 17. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 32715790 Review.
-
The Role of Gastrointestinal Microbiota in Functional Dyspepsia: A Review.Front Physiol. 2022 Jun 8;13:910568. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.910568. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35755434 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on functional dyspepsia and irritable bowel syndrome: A population-based survey.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 Jul;36(7):1820-1827. doi: 10.1111/jgh.15346. Epub 2020 Dec 1. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 33197076 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence that independent gut-to-brain and brain-to-gut pathways operate in the irritable bowel syndrome and functional dyspepsia: a 1-year population-based prospective study.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2016 Sep;44(6):592-600. doi: 10.1111/apt.13738. Epub 2016 Jul 22. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2016. PMID: 27444264
-
Anxiety is associated with uninvestigated and functional dyspepsia (Rome III criteria) in a Swedish population-based study.Gastroenterology. 2009 Jul;137(1):94-100. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.03.039. Epub 2009 Mar 26. Gastroenterology. 2009. PMID: 19328797
Cited by
-
Factors Predicting Effectiveness of Eradication Therapy for Helicobacter pylori-Associated Dyspepsia Symptoms.Life (Basel). 2024 Jul 25;14(8):935. doi: 10.3390/life14080935. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39202677 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection among dyspeptic patients attending Baghdad medical city complex.Iran J Microbiol. 2025 Jun;17(3):397-403. doi: 10.18502/ijm.v17i3.18822. Iran J Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40612735 Free PMC article.
-
Putting Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders within the Spectrum of Inflammatory Disorders Can Improve Classification and Diagnostics of These Disorders.Biomedicines. 2024 Mar 21;12(3):702. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12030702. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38540315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A bibliometric analysis of interstitial cells of Cajal research.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 May 20;11:1391545. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1391545. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38831987 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sperber A.D., Bangdiwala S.I., Drossman D.A., Ghoshal U.C., Simren M., Tack J., Whitehead W.E., Dumitrascu D.L., Fang X., Fukudo S., et al. Worldwide Prevalence and Burden of Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders, Results of Rome Foundation Global Study. Gastroenterology. 2021;160:99–114.e3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.04.014. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Klaassen T., Vork L., Smeets F.G.M., Troost F.J., Kruimel J.W., Leue C., Masclee A.A.M., Keszthelyi D. The Interplay between Stress and Fullness in Patients with Functional Dyspepsia and Healthy Controls: An Exploratory Experience Sampling Method Study. Psychosom. Med. 2022;84:306–312. doi: 10.1097/PSY.0000000000001012. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

