Serelaxin Protects H9c2 Cardiac Myoblasts against Hypoxia and Reoxygenation-Induced Damage through Activation of AMP Kinase/Sirtuin1: Further Insight into the Molecular Mechanisms of the Cardioprotection of This Hormone
- PMID: 38397761
- PMCID: PMC10886064
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox13020163
Serelaxin Protects H9c2 Cardiac Myoblasts against Hypoxia and Reoxygenation-Induced Damage through Activation of AMP Kinase/Sirtuin1: Further Insight into the Molecular Mechanisms of the Cardioprotection of This Hormone
Abstract
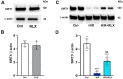
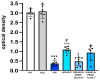
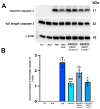
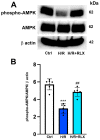
Serelaxin (RLX), namely the human recombinant Relaxin-2 hormone, protects the heart from ischemia/reperfusion (I/R)-induced damage due to its anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic and antioxidant properties. RLX acts by binding to its specific RXFP1 receptor whereby it regulates multiple transduction pathways. In this in vitro study, we offer the first evidence for the involvement of the AMP kinase/Sirtuin1 (AMPK/SIRT1) pathway in the protection by RLX against hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R)-induced damage in H9c2 cells. The treatment of the H/R-exposed cells with RLX (17 nmol L-1) enhanced SIRT1 expression and activity. The inhibition of SIRT1 signaling with EX527 (10 µmol L-1) reduced the beneficial effect of the hormone on mitochondrial efficiency and cell apoptosis. Moreover, RLX upregulated the AMPK pathway, as shown by the increase in the expression of phospho-AMPK-activated protein. Finally, AMPK pathway inhibition by Compound C (10 and 20 μmol L-1) abrogated the increase in SIRT1 expression induced by RLX, thus suggesting the involvement of the AMPK pathway in this effect of RLX. These results strengthen the concept that RLX exerts its cardioprotective effects against H/R-induced injury through multiple pathways which also include AMPK/SIRT1. These new findings support the use of RLX or RLX-derived molecules as a promising therapeutic for those diseases in which I/R and oxidative stress play a pathogenic role.
Keywords: AMPK; H9c2 cells; SIRT1; Serelaxin; apoptosis; hypoxia–reoxygenation; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Human Relaxin-2 (Serelaxin) Attenuates Oxidative Stress in Cardiac Muscle Cells Exposed In Vitro to Hypoxia-Reoxygenation. Evidence for the Involvement of Reduced Glutathione Up-Regulation.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Aug 21;9(9):774. doi: 10.3390/antiox9090774. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32825567 Free PMC article.
-
Relaxin protects cardiac muscle cells from hypoxia/reoxygenation injury: involvement of the Notch-1 pathway.FASEB J. 2015 Jan;29(1):239-49. doi: 10.1096/fj.14-254854. Epub 2014 Oct 23. FASEB J. 2015. PMID: 25342127
-
Schizandrin B attenuates hypoxia/reoxygenation injury in H9c2 cells by activating the AMPK/Nrf2 signaling pathway.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Mar;21(3):220. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.9651. Epub 2021 Jan 18. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 33603829 Free PMC article.
-
CTRP13 Protects H9c2 Cells Against Hypoxia/Reoxygenation (H/R)-Induced Injury Via Regulating the AMPK/Nrf2/ARE Signaling Pathway.Cell Transplant. 2021 Jan-Dec;30:9636897211033275. doi: 10.1177/09636897211033275. Cell Transplant. 2021. PMID: 34338573 Free PMC article.
-
Relaxin in hepatic fibrosis: What is known and where to head?Biochimie. 2021 Aug;187:144-151. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2021.06.001. Epub 2021 Jun 5. Biochimie. 2021. PMID: 34102254 Review.
Cited by
-
Protective Role of Oxycodone in Myocardial Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction Induced by Ischemia-Reperfusion.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2025 Feb;39(2):e70151. doi: 10.1002/jbt.70151. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 39865943 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

