Regulation of P-Glycoprotein during Oxidative Stress
- PMID: 38397813
- PMCID: PMC10885963
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox13020215
Regulation of P-Glycoprotein during Oxidative Stress
Abstract
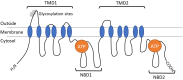
P-glycoprotein (Pgp, ABCB1, MDR1) is an efflux transporter protein that removes molecules from the cells (outflow) into the extracellular space. Pgp plays an important role in pharmacokinetics, ensuring the absorption, distribution, and excretion of drugs and its substrates, as well as in the transport of endogenous molecules (steroid and thyroid hormones). It also contributes to tumor cell resistance to chemotherapy. In this review, we summarize the mechanisms of Pgp regulation during oxidative stress. The currently available data suggest that Pgp has a complex variety of regulatory mechanisms under oxidative stress, involving many transcription factors, the main ones being Nrf2 and Nf-kB. These factors often overlap, and some can be activated under certain conditions, such as the deposition of oxidation products, depending on the severity of oxidative stress. In most cases, the expression of Pgp increases due to increased transcription and translation, but under severe oxidative stress, it can also decrease due to the oxidation of amino acids in its molecule. At the same time, Pgp acts as a protector against oxidative stress, eliminating the causative factors and removing its by-products, as well as participating in signaling pathways.
Keywords: Nf-kB; Nrf2; P-glycoprotein; oxidative stress; reactive oxygen species.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Glucose modulation induces reactive oxygen species and increases P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance to chemotherapeutics.Br J Pharmacol. 2015 May;172(10):2557-72. doi: 10.1111/bph.13079. Epub 2015 Mar 17. Br J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25586174 Free PMC article.
-
Dual regulation of P-glycoprotein expression by trichostatin A in cancer cell lines.BMC Mol Biol. 2012 Jul 30;13:25. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-13-25. BMC Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22846052 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, molecular structure, and validation of metalloprobes for assessment of MDR1 P-glycoprotein-mediated functional transport.Dalton Trans. 2010 Jul 7;39(25):5842-50. doi: 10.1039/c002361b. Epub 2010 May 27. Dalton Trans. 2010. PMID: 20505882
-
Modulation and prevention of multidrug resistance by inhibitors of P-glycoprotein.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1997;40 Suppl:S13-9. doi: 10.1007/s002800051055. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9272128 Review.
-
Multidrug resistance: molecular mechanisms and clinical relevance.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1997;40 Suppl:S3-8. doi: 10.1007/s002800051053. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9272126 Review.
Cited by
-
Acridine-Based Chalcone 1C and ABC Transporters.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 27;26(9):4138. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094138. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362377 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning combined multi-omics analysis to explore key oxidative stress features in systemic lupus erythematosus.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 20;16:1567466. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1567466. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40625749 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Doxorubicin Chemotherapy: Emerging Polymeric Nanocarriers for Drug Loading and Delivery.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jul 10;17(14):2303. doi: 10.3390/cancers17142303. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40723187 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alterations in P-glycoprotein Expression in the Placenta of Obese Rats and Humans.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 20;26(14):6976. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146976. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40725223 Free PMC article.
-
The Dual Role of NRF2 in Colorectal Cancer: Targeting NRF2 as a Potential Therapeutic Approach.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Sep 4;17:5985-6004. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S479794. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39247839 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

