Advances in Pharmacological Approaches for Managing Hypercholesterolemia: A Comprehensive Overview of Novel Treatments
- PMID: 38398034
- PMCID: PMC10887105
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12020432
Advances in Pharmacological Approaches for Managing Hypercholesterolemia: A Comprehensive Overview of Novel Treatments
Abstract
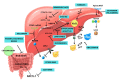
Hypercholesterolemia plays a crucial role in the formation of lipid plaques, particularly with elevated low-density lipoprotein (LDL-C) levels, which are linked to increased risks of cardiovascular disease, cerebrovascular disease, and peripheral arterial disease. Controlling blood cholesterol values, specifically reducing LDL-C, is widely recognized as a key modifiable risk factor for decreasing the morbidity and mortality associated with cardiovascular diseases. Historically, statins, by inhibiting the enzyme β-hydroxy β-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG)-CoA reductase, have been among the most effective drugs. However, newer non-statin agents have since been introduced into hypercholesterolemia therapy, providing a viable alternative with a favorable cost-benefit ratio. This paper aims to delve into the latest therapies, shedding light on their mechanisms of action and therapeutic benefits.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; cardiovascular disease; hypercholesterolemia; lipid-lowering drugs; statins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sasso F.C., Simeon V., Galiero R., Caturano A., De Nicola L., Chiodini P., Rinaldi L., Salvatore T., Lettieri M., Nevola R., et al. The number of risk factors not at target is associated with cardiovascular risk in a type 2 diabetic population with albuminuria in primary cardiovascular prevention. Post-hoc analysis of the NID-2 trial. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2022;21:235. doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01674-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Caturano A., D’Angelo M., Mormone A., Russo V., Mollica M.P., Salvatore T., Galiero R., Rinaldi L., Vetrano E., Marfella R., et al. Oxidative Stress in Type 2 Diabetes: Impacts from Pathogenesis to Lifestyle Modifications. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023;45:6651–6666. doi: 10.3390/cimb45080420. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources