Multimodality Imaging in Right Heart Tumors: Proposed Algorithm towards an Appropriate Diagnosis
- PMID: 38398314
- PMCID: PMC10888584
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13041000
Multimodality Imaging in Right Heart Tumors: Proposed Algorithm towards an Appropriate Diagnosis
Abstract
A right heart tumor can be identified by transthoracic echocardiography during a routine examination or due to cardiac symptoms. The first step is the assessment by echocardiography, with its multiple techniques, and the obtained information must be judged in a clinical and biological context. The second step comprises one, sometimes even two, of the more complex modality imaging methods. The choice is driven not only by the advantages of each imaging technique but also by local expertise or the preferred imaging modality in the center. This step is followed by staging, follow-up, and/or imaging-guided excision or biopsy, which is performed in selected cases in order to obtain anatomopathological confirmation. In the presence of features suggestive of malignancy or causing hemodynamic impairment, a transvenous biopsy is essential before the more complex imaging modalities (which are still relevant in the staging process). Using a structured imaging approach, it is possible to reach an appropriate diagnosis without a biopsy. Frequently, these imaging techniques have a complementary role, so an integrated imaging approach is recommended. This proposed algorithm for appropriate diagnosis of right heart tumors could serve as a practical guide for clinicians (not only imaging specialists).
Keywords: cardiac magnetic resonance; computer tomography; echocardiography; imaging; multimodality; positron emission tomography; right heart; tumor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




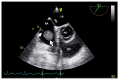
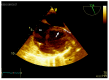
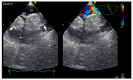
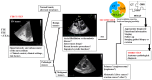
References
-
- Han B.K., Rigsby C.K., Leipsic J., Bardo D., Abbara S., Ghoshhajra B., Lesser J.R., Raman S.V., Crean A.M., Nicol E.D., et al. Computed Tomography Imaging in Patients with Congenital Heart Disease, Part 2: Technical Recommendations. An Expert Consensus Document of the Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography (SCCT): Endorsed by the Society of Pediatric Radiology (SPR) and the North American Society of Cardiac Imaging (NASCI) J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2015;9:493–513. - PubMed
-
- Secinaro A., Ait-Ali L., Curione D., Clemente A., Gaeta A., Giovagnoni A., Alaimo A., Esposito A., Tchana B., Sandrini C., et al. Recommendations for cardiovascular magnetic resonance and computed tomography in congenital heart disease: A consensus paper from the CMR/CCT working group of the Italian Society of Pediatric Cardiology (SICP) and the Italian College of Cardiac Radiology endorsed by the Italian Society of Medical and Interventional Radiology (SIRM) Part I. Radiol. Med. 2022;127:788–802. doi: 10.1007/s11547-022-01490-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

