Polyps' Extension and Recurrence in Different Endotypes of Chronic Rhinosinusitis: A Series of 449 Consecutive Patients
- PMID: 38398437
- PMCID: PMC10889470
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13041125
Polyps' Extension and Recurrence in Different Endotypes of Chronic Rhinosinusitis: A Series of 449 Consecutive Patients
Abstract
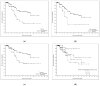
Different inflammatory endotypes reflect the heterogeneity of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps' (CRSwNPs) clinical presentation. This retrospective study aimed to analyze the distribution of polyps in nasal cavities and paranasal sinuses to establish a possible association between CRSwNP endotypes, prognosis, and polyps' extension. This study included 449 adult patients who underwent endoscopic sinus surgery for CRSwNPs between 2009 and 2022. Patients were categorized based on the number of paranasal sinuses involved by polyps. Statistical analyses, including Cox regression, were performed to identify associations between demographic, clinical, and histopathological factors and disease recurrence. CRSwNP patients were stratified into four groups based on the extent of polyp involvement. Asthma and acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) sensitivity were associated with more sinuses involved (p-values = 0.0003 and 0.0037, respectively). Blood eosinophil counts increased with the number of sinuses affected (p-value < 0.0001). The distribution of eosinophilic and non-eosinophilic histotypes varied significantly among these groups (p-value < 0.0001). The risk of CRSwNP recurrence was higher in patients with asthma, higher basophil percentages, and eosinophilic histotype (p-value 0.0104, 0.0001, 0.0118, and 0.0104, respectively). This study suggests a positive association between the number of paranasal sinuses involved by polyps and the severity of CRSwNPs, particularly in patients with eosinophilic histotype, asthma, and ASA sensitivity.
Keywords: ASA intolerance; CRSwNP; ESS; asthma; basophils; endotypes; eosinophils.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Blood Eosinophil and Basophil Values Before and After Surgery for Eosinophilic-type Sinonasal Polyps.Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2018 May;32(3):194-201. doi: 10.1177/1945892418768590. Epub 2018 Apr 20. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2018. PMID: 29676185
-
Non-Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis With Nasal Polyps: Eosinophil, Basophil, and Neutrophil Blood Counts Before and After Surgery.Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2019 Mar;128(3):233-240. doi: 10.1177/0003489418818578. Epub 2018 Dec 17. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2019. PMID: 30556407
-
Eosinophilic and Non-eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps and Their Clinical Comparison in Indian Population.Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2022 Oct;74(Suppl 2):994-1000. doi: 10.1007/s12070-020-02062-x. Epub 2020 Aug 19. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2022. PMID: 36452721 Free PMC article.
-
Role of blood inflammatory cells in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps.Acta Otolaryngol. 2019 Jan;139(1):48-51. doi: 10.1080/00016489.2018.1538567. Epub 2019 Jan 28. Acta Otolaryngol. 2019. PMID: 30686139 Review.
-
Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps in the elderly: Assessing current evidence.Allergy Asthma Proc. 2018 Jan 1;39(1):9-13. doi: 10.2500/aap.2018.39.4101. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2018. PMID: 29279055 Review.
Cited by
-
Risk factors for postoperative recurrence in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: development of a prediction model.Am J Transl Res. 2024 Oct 15;16(10):5477-5486. doi: 10.62347/UJWU7059. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 39544768 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of CNPase and TGFβ1/Smad Signalling Pathway Molecule Expression in Sinus Epithelial Tissues of Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis with (CRSwNP) and without Nasal Polyps (CRSsNP).J Pers Med. 2024 Aug 23;14(9):894. doi: 10.3390/jpm14090894. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 39338148 Free PMC article.
References
-
- La Mantia I., Grigaliute E., Ragusa M., Cocuzza S., Radulesco T., Saibene A.M., Calvo-Henriquez C., Fakhry N., Michel J., Maniaci A. Effectiveness and rapidity on olfatory fuction recovery in CRS patients treated with Dupilumab: A real life prospective controlled study. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2024;281:219–226. doi: 10.1007/s00405-023-08184-6. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

