The Effect and Mechanism of Oleanolic Acid in the Treatment of Metabolic Syndrome and Related Cardiovascular Diseases
- PMID: 38398510
- PMCID: PMC10892503
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29040758
The Effect and Mechanism of Oleanolic Acid in the Treatment of Metabolic Syndrome and Related Cardiovascular Diseases
Abstract
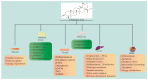
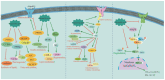
Metabolic syndromes (MetS) and related cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) pose a serious threat to human health. MetS are metabolic disorders characterized by obesity, dyslipidemia, and hypertension, which increase the risk of CVDs' initiation and development. Although there are many availabile drugs for treating MetS and related CVDs, some side effects also occur. Considering the low-level side effects, many natural products have been tried to treat MetS and CVDs. A five-cyclic triterpenoid natural product, oleanolic acid (OA), has been reported to have many pharmacologic actions such as anti-hypertension, anti-hyperlipidemia, and liver protection. OA has specific advantages in the treatment of MetS and CVDs. OA achieves therapeutic effects through a variety of pathways, attracting great interest and playing a vital role in the treatment of MetS and CVDs. Consequently, in this article, we aim to review the pharmacological actions and potential mechanisms of OA in treating MetS and related CVDs.
Keywords: cardiovascular diseases; metabolic syndrome; oleanolic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Fishel Bartal M., Blackwell S.C., Pedroza C., Lawal D., Amro F., Samuel J., Chauhan S.P., Sibai B.M. Oral combined hydrochlorothiazide and lisinopril vs nifedipine for postpartum hypertension: A comparative-effectiveness pilot randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2023;228:571.e1–571.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2023.01.015. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Davidsen L., Jensen M.H., Cook M.E., Vestergaard P., Knop F.K., Drewes A.M., Olesen S.S. Metformin treatment is associated with reduced risk of hypoglycaemia, major adverse cardiovascular events, and all-cause mortality in patients with post-pancreatitis diabetes mellitus: A nationwide cohort study. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2024;190:44–53. doi: 10.1093/ejendo/lvad175. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- No. 2022SK2011/Key Research and Development Projects of the Hunan Provincial Science and Technology Department
- No. 2021RC4064/Science and Technology Innovation team of the Hunan Province
- No. 20A379/Key Projects of the Hunan Provincial Department of Education
- No. 2023CX163/Graduate Innovation Project of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine
- No. 22B0387/Excellent Youth Project of the Hunan Provincial Department of Education
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

